Arrested, seized, doxed and detained. These are just some of the ways police and prosecutors around the world took down the biggest cybercrime operations of the year, even if it meant resorting to new and unconventional eyebrow-raising methods. From stashing billions of bitcoin under the floorboards to teenage hackers gatecrashing Fortune 500 networks, this year saw some of the most jaw-dropping breaches — and the highest-profile apprehensions.
As we close out 2022, we look back at the cybercriminals we lost this year … to the law.
Sanctions and seizures hit the crypto scene
U.S. officials scored some major wins against crypto-laundering in 2022. At the beginning of the year, the Justice Department said it had seized more than $3.6 billion worth of bitcoins allegedly stolen in the 2016 hack of crypto exchange Bitfinex and that it had arrested a married couple suspected of laundering the money.
The couple — Ilya Lichtenstein, 34, and Heather Morgan, 31 — face up to 25 years in prison if convicted on charges of conspiring to launder money and defrauding the U.S. government.
Later in the year, the Office of Foreign Asset Control (OFAC), a watchdog within the U.S. Treasury tasked with enforcing sanctions violations, announced that it had sanctioned decentralized cryptocurrency mixing service Tornado Cash for its role in enabling billions of dollars’ worth of cryptocurrency to be laundered through its platform.
Tornado Cash, along with other mixers such as AlphaBay, allows customers to conceal the source of their crypto funds when participating in a transaction in exchange for a fee. It blends potentially identifiable or tainted cryptocurrency funds with others to obfuscate the source and destination of crypto assets. More than $1.5 billion in proceeds of crime, like ransomware and fraud, has been laundered through Tornado Cash to date, experts estimate.
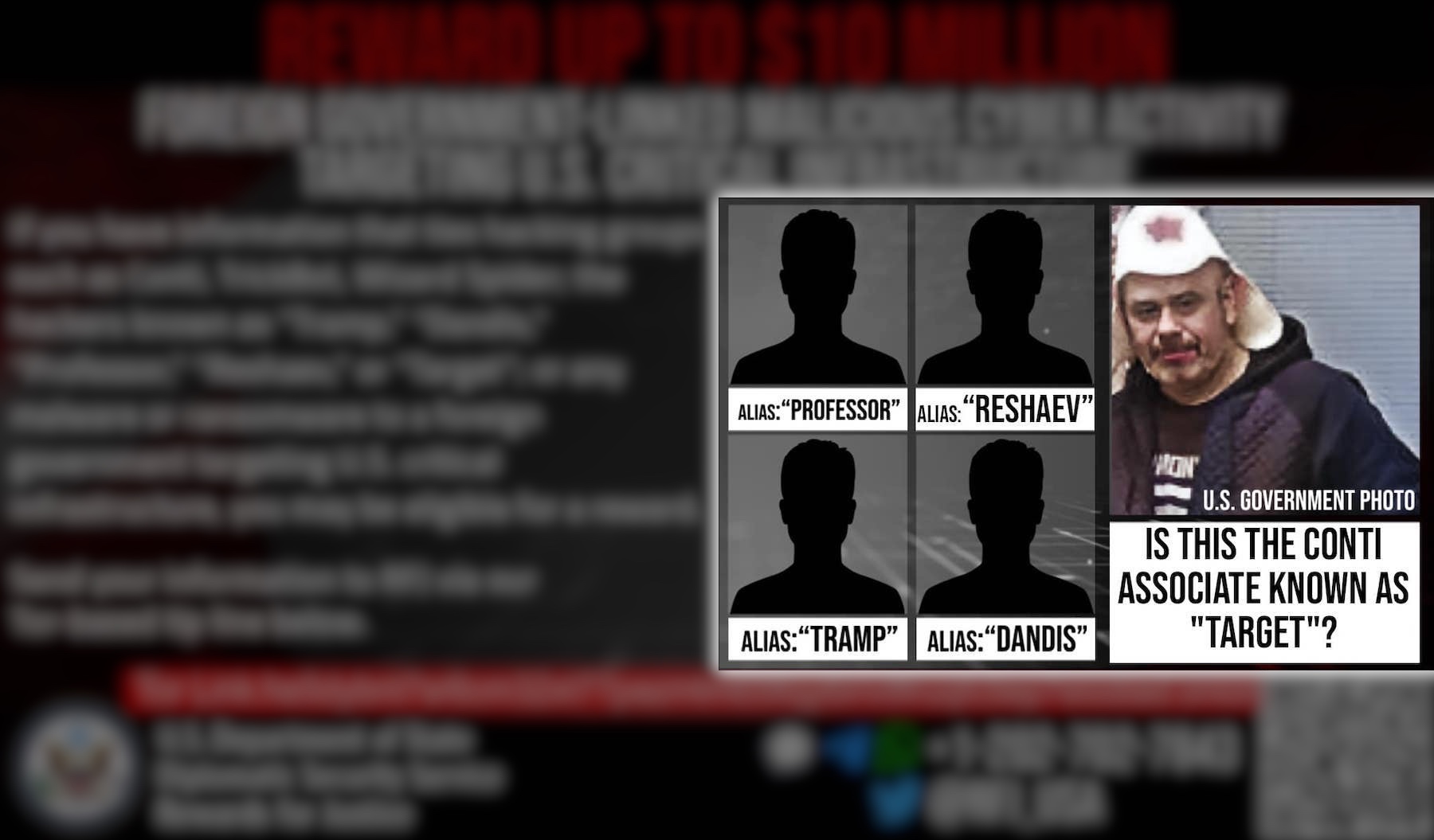
U.S. doxes alleged Conti ransomware member
In August, the U.S government shared an image of a suspected Conti ransomware operator known as “Target,” the first time it has outed a major ransomware actor. The program also offered up to $10 million for information leading to the identification and location of Target, along with four other alleged Conti members known as “Tramp,” “Dandis,” “Professor” and “Reshaev.”
The State Department said Conti has carried out more than 1,000 ransomware operations targeting U.S. and international critical infrastructure. Most recently, the gang infiltrated 27 government institutions in Costa Rica and demanded a $20 million ransom.
Another gang dealt a devastating hit in 2022 was NetWalker, a ransomware gang that has been linked to numerous high-profile incidents including an attack on the University of California San Francisco, which paid a ransom demand of more than $1 million, and an attack targeting cyberthreat startup Cygilant. Between August 2019 and January 2021, ransomware attacks involving NetWalker pulled $46 million in ransom payments, according to cryptocurrency analysis firm Chainalysis.
In October, Sebastien Vachon-Desjardins, a 34-year-old from Quebec, was sentenced in a Florida court in October after pleading guilty to charges related to his involvement with NetWalker. Vachon-Desjardins, who worked as an IT consultant for Public Works and Government Services in Canada, was previously arrested by Canadian police in January 2021 and sentenced to seven years in prison. During a search of his home, law enforcement officials discovered and seized 719 bitcoin and $790,000 in Canadian currency.
James Zhong, the hacker who stole billions of Silk Road’s bitcoin
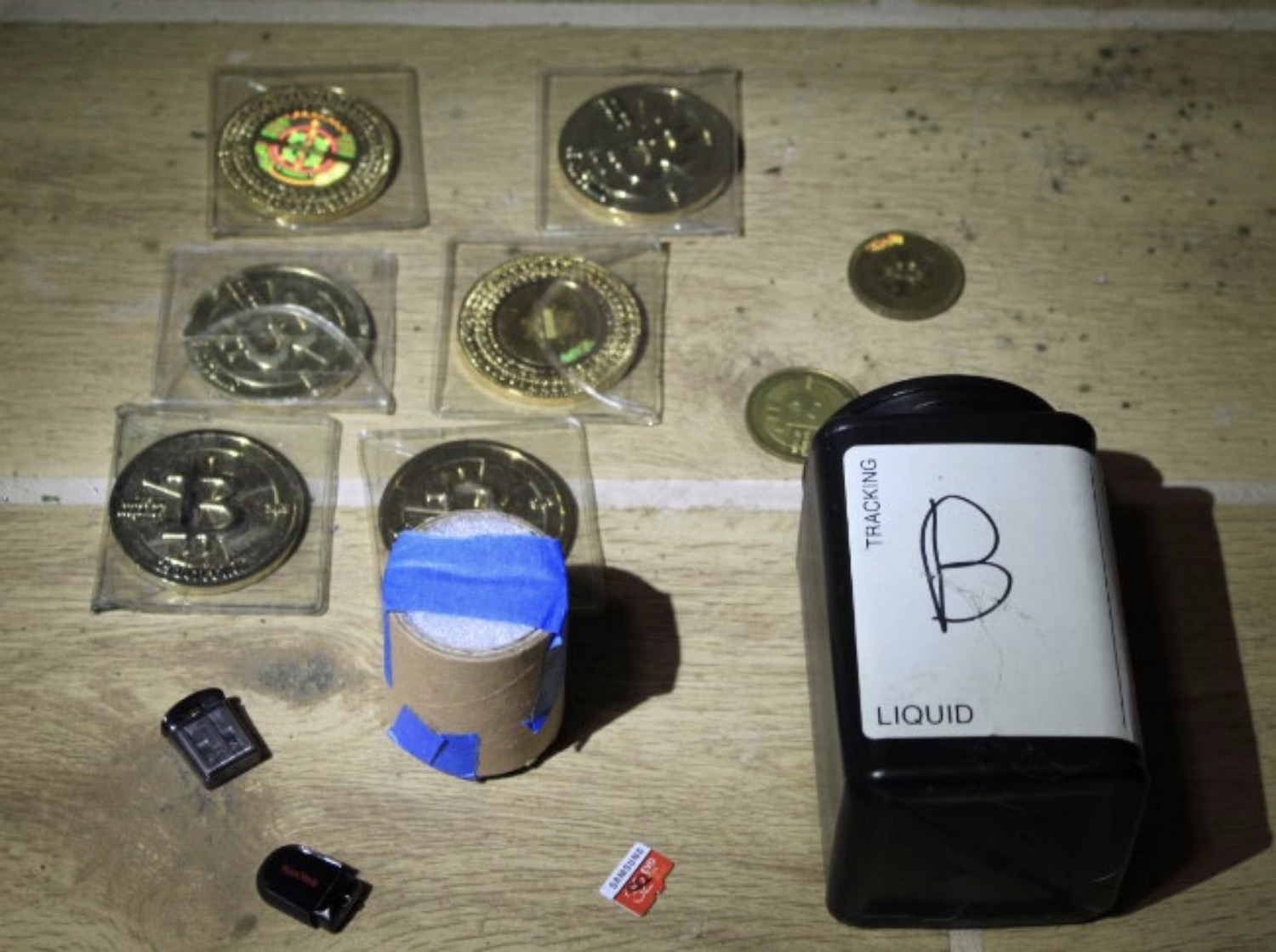
In a surprising yet anticlimactic conclusion to one of the government’s longest-running cyber cases, the mystery of the notorious dark web drugs marketplace Silk Road’s missing billions was solved. In November, U.S. federal agents said it found $3.36 billion worth of bitcoin that had been stashed in a popcorn can under the bathroom closet floorboards in the home of the hacker nearly a decade earlier. Prosecutors brought charges against the hacker, a Georgia resident named James Zhong, whose plea agreement with the feds saw him forfeit the huge cache of cryptocurrency, along with $600,000 in cash and other precious metals.
Somewhat confusingly, Zhong is the second hacker to have ultimately turned over Silk Road’s stolen billions — albeit at a lower exchange rate than today. In 2020, a hacker who went by the alias Individual X forfeited another huge cache of Silk Road’s bitcoin that they had stolen years earlier during a hacking spree over 2012 and 2013. The Justice Department’s latest forfeiture closed the door on another billion-dollar mystery, even if the feds kept secret how the funds were stolen or how they came to find the hacker, long after Silk Road’s founder Ross Ulbricht was jailed.

Raccoon Stealer operator charged over mass password theft
U.S. officials in October charged a Ukrainian national over his alleged role in the Raccoon Infostealer malware-as-a-service operation that infected millions of computers worldwide. Mark Sokolovsky, who goes by the online handle “raccoonstealer,” is accused of having a major role as a key administrator of the malware, which prosecutors say was used to steal more than 50 million unique credentials and forms of identification from victims around the world since February 2019.
Sokolovsky is charged with computer fraud, wire fraud, money laundering and identity theft and faces up to 20 years in prison if found guilty. Sokolovsky is in Amsterdam awaiting extradition to the United States.
Sokolvsky’s arrest led to an uptick in new Mars Stealer campaigns, including the mass-targeting of Ukraine in the weeks following Russia’s invasion and a large-scale effort to infect victims by malicious ads. However, in November, a security research and hacking startup told TechCrunch that it had found a coding flaw that allows it to lock out operators of the Mars Stealer malware from their own servers and release their victims.
Seller of WhatsApp-hacking tech pleads guilty
Signal jammers, Wi-Fi interception tools and WhatsApp hacking tools. These are some of the things that one Mexican businessman admitted in federal court to selling for both commercial and personal reasons. The Justice Department accused Carlos Guerrero of, among other things, arranging the sale of hacking tools to Mexican politicians and using other equipment he sold to intercept the phone calls of a U.S. rival. It goes to show that it’s not just nation states and governments with powerful phone spying technology at their disposal.
Lapsus$ rounded up once, twice
The Lapsus$ gang rose to notoriety in 2022. The data extortion group, which first emerged a year earlier, quickly claimed a number of high-profile victims, including Okta, Microsoft, Nvidia and Samsung.
While the gang once seemed invincible, a number of its members were arrested in March this year. In a statement given to TechCrunch at the time, City of London Police confirmed that seven people between the ages of 16 and 21 had been arrested in connection with Lapsus$.
News of the arrests came just hours after a Bloomberg report revealed a teenager based in Oxfordshire, U.K. is suspected of being the mastermind of the Lapsus$ group. Researchers investigating the gang’s recent hacks said they believed the 16-year-old, who uses the online moniker “White” or “Breachbase,” was a leading figure in Lapsus$. Bloomberg was able to track down the suspected hacker after his personal information was published online by rival hackers. Weeks later, U.K. police said they had charged two of the teenagers with multiple cyber offenses.
SSNDOB, a marketplace for stolen Social Security numbers, is no more
U.S. officials in June announced the takedown of SSNDOB, a notorious marketplace used for trading the personal information — including Social Security numbers, or SSNs — of millions of Americans.
The landmark operation was carried out by the FBI, IRS and the DOJ, with help from the Cyprus Police, and saw authorities seize four domains hosting the SSNDOB marketplace.
SSNDOB listed the personal information for approximately 24 million individuals in the United States, including names, dates of birth, SSNs and credit card numbers and generated more than $19 million in revenue, according to prosecutors. Chainalysis reported separately that the marketplace has received nearly $22 million worth of bitcoin over 100,000 transactions since April 2015, though the marketplace is believed to have been active for several years prior to its eventual seizure.

Ex-Amazon engineer convicted of Capital One data heist
Also in June, Paige Thompson, a former engineer in Amazon’s cloud division, was convicted of a breach that compromised the personal and financial information of 100 million CapitalOne customers in 2019. The breach was one of the biggest bank heists in U.S. history, which included the theft of credit scores, limits and balances, and also affected a million Canadians. Thompson was accused of using her knowledge as an Amazon software engineer to breach CapitalOne’s online cloud storage, hosted on Amazon’s servers, and compromising the cloud storage of several other companies, including Vodafone, Ford and Ohio’s state motor vehicle agency. Prosecutors said the former Amazon engineer was “one bad day away from sharing the data she stole.” As such, Thompson was sentenced to time served, allowing her to avoid prison.
A major REvil operator was extradited to the United States
With a $10 million bounty on their heads after a brazen ransomware attack on Kaseya that spread to hundreds of its downstream customers, it was only a matter of time before the REvil ransomware group’s luck would run out. That’s what happened with Yaroslav Vasinskyi, a 22-year-old Ukrainian national, who was arrested in Poland in October and later arraigned and extradited to Dallas, Texas to face accusations of computer hacking and fraud by way of his alleged involvement with REvil. Vasinskyi is one of two other alleged REvil members charged by U.S. prosecutors in relation to the attack on Kaseya. It was only after the FBI recovered the decryption key that victims were able to gain access back to their encrypted files.
U.K. arrest teenagers linked to Uber and GTA hacks
In September, police in London confirmed that a 17-year-old teenager suspected of involvement in high-profile breaches at ride-hailing giant Uber and Rockstar Games had been charged with multiple counts of computer misuse and breaches of bail.
These hacks were two of the most high-profile of 2022. Uber, which said it believed a hacker affiliated with Lapsus$ was responsible for the attack, was forced to take several of its internal tools offline while it expelled the hacker from its network. Shortly before Uber’s Slack system was taken offline, Uber employees received a message that read, “I announce I am a hacker and Uber has suffered a data breach.” The hacker also reportedly said that Uber drivers should receive higher pay.
In the case of Rockstar Games, the attacker — who also goes by the alias “TeaPot” — claimed to have gained access to Rockstar Games’ internal messages on Slack and early code for an unannounced Grand Theft Auto sequel by gaining access to an employee’s login credentials.
It’s all in the (lack of) details: 2022’s badly handled data breaches






























Comment