Nielsen’s U.S. music report on the first half of 2014 shows digital music consumption rapidly shifting from downloads to streaming. On-demand streaming was up 42% over the first half of 2013, racking up 70 billion play in the first half of 2014. Meanwhile, digital track sales fell 13% to 593.6 million and album sales fell 11.6% to 53.8 million. The report on US trends (not international) makes Apple’s acquisition of Beats looks smart, as its iTunes download sales model is quickly dying out. As a whole, dismal digital and physical sales dragged total music sales plus streaming industry down 3.3%.
Back in the analog world, hipsters are making a serious impact as vinyl sales rose 40% over 2013 to 4 million in the first half of this year. That’s the only medium where sales grew.
[Update: It’s important to note that abroad, where iTunes is available in 83+ countries and streaming services often aren’t, the download may survive longer.]
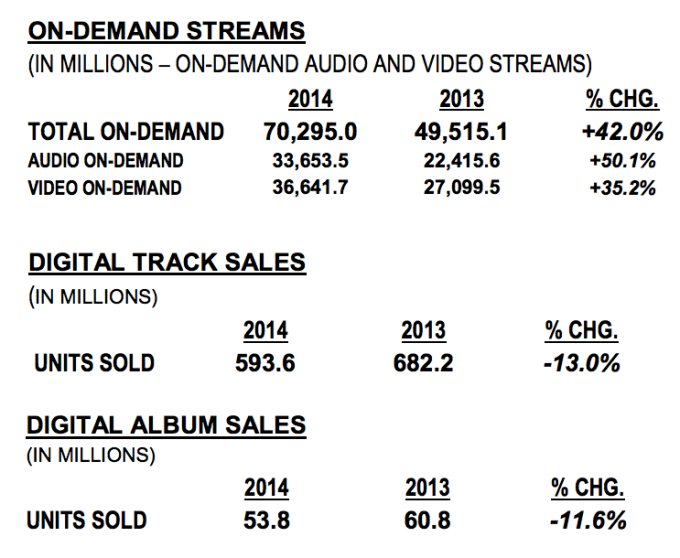
If you use the standard 10X multiplier convert album sales to tracks, you get a combined 1.131 billion songs sold in the first half of 2014, down 12% from that period in 2013.
While YouTube’s music videos have been strong provider of music streaming for years, the rise of apps like Spotify is pushing on-demand audio music streaming to grow faster (+50%) than video (+35%). The two are now nearly the same size, as 33.65 billion songs were streamed in the first half of 2014, compared to 36.64 billion music video streams. At this rate, pure audio streaming will overcome music video streaming in the U.S. by the end of 2014. Internationally, where many of the top streaming apps aren’t always available, YouTube is probably still a bigger chunk of consumption.
You can see Nielsen’s full report here:
The State Of MusicTech
The music industry’s rapid recent changes make more sense after looking at this report. With the death of the download and the rise of the stream, power is up for grabs. While iTunes and to a lesser extent Amazon ruled the age of the legal download, Spotify, Google Music, and Beats are poised to reign over the streaming era.
 That’s why Apple bought Beats. A source close to iTunes’ executives told me before the acquisition that Apple didn’t want to shock users and the music industry’s bottom line by suddenly converting iTunes into a streaming service. Instead, it bought Beats to allow for a graceful transition, permitting late-adopters to stick with the familiar a la carte download model while early adopters moved to Beats’ all-you-can-hear streaming subscription.
That’s why Apple bought Beats. A source close to iTunes’ executives told me before the acquisition that Apple didn’t want to shock users and the music industry’s bottom line by suddenly converting iTunes into a streaming service. Instead, it bought Beats to allow for a graceful transition, permitting late-adopters to stick with the familiar a la carte download model while early adopters moved to Beats’ all-you-can-hear streaming subscription.
Google just acquired contextual playlist app Songza to bolster its bolster its on-demand Google Music All-Access streaming service. Google’s combatant looked a bit dry before, especially compared to Beats’ focus on expertly crafted playlists for different themes, situations, and moods. Now Google Music has a more human understanding of what people want to hear and when.
Spotify has raised over a half a billion dollars, making it too big to buy for all but the biggest players like Google, Microsoft, and Facebook. At this rate it’s going to fly independent into an IPO, though that could be tough to sell since it’s saddled with high royalty rates that scale alongside it’s popularity. Spotify bought data provider EchoNest earlier this year, and is now experimenting with an API that let’s users play their Spotify music through third-party apps. Becoming the legal backbone of music streaming in tons of apps could make its subscription more attractive to users, and I see developing an ecosystem of niche music apps around it as high-potential way to fight the platform owners.
 Samsung is trying to popularize its own device-specific music service with Milk, but since its phones run Android, it highly vulnerable to Google’s native offering. While Pandora still has a huge user base, personalized radio has been commoditized and bolted on in the form of iTunes Radio and Spotify’s ad-supported version. Meanwhile, Pandora’s licensing model doesn’t allow it to offer on-demand song choices like they do, which is why I foresee it struggling in years to come.
Samsung is trying to popularize its own device-specific music service with Milk, but since its phones run Android, it highly vulnerable to Google’s native offering. While Pandora still has a huge user base, personalized radio has been commoditized and bolted on in the form of iTunes Radio and Spotify’s ad-supported version. Meanwhile, Pandora’s licensing model doesn’t allow it to offer on-demand song choices like they do, which is why I foresee it struggling in years to come.
SoundCloud offers on-demand streaming of songs and long mixtapes that users and artists upload themselves. It’s seen labels cracking down on unlicensed streaming through the app, which is trying to build out its own advertising system. While music fans view it as an authentic place to connect with artists, it’s still figuring out how to become a succesful business. The “YouTube of music” might benefit from being acquired, though Twitter recently passed on the idea, which I believe was because it needed to spend the money to get its own monetization squared away by buying ad tech companies instead.
 Amazon just launched its Prime Music on-demand service. But rather than trying to win over serious music fans, it’s using it to simply add value to Prime subscriptions that help it earn money by selling physical goods. It’s more of a threat to services courting casual listeners like Pandora who just want to hear something and aren’t too picky. YouTube is expected to launch its on-demand music streaming subscription service soon as a complement to its ad supported music video streaming that gets little press but is extremely popular, especially with kids. While the on-demand service has a tough uphill climb ahead given Google already has its native Music All-Access service to promote, its free browser-based videos reduce the need to pay for a dedicated music app.
Amazon just launched its Prime Music on-demand service. But rather than trying to win over serious music fans, it’s using it to simply add value to Prime subscriptions that help it earn money by selling physical goods. It’s more of a threat to services courting casual listeners like Pandora who just want to hear something and aren’t too picky. YouTube is expected to launch its on-demand music streaming subscription service soon as a complement to its ad supported music video streaming that gets little press but is extremely popular, especially with kids. While the on-demand service has a tough uphill climb ahead given Google already has its native Music All-Access service to promote, its free browser-based videos reduce the need to pay for a dedicated music app.
In 15 years we’ve gone from CDs to Napster piracy to iTunes downloads to Pandora radio to YouTube’s music video streaming to Spotify’s audio streaming app. Perhaps the next shift will finally see the labels loosen their death grips and allow a cornucopia of music discovery apps to flourish atop a few legal rights holders so everyone can get a listening experience that’s their jam.
