Last week was a good one for edtech in Europe.
GoStudent became Europe’s first edtech unicorn (IPO’d companies aside), raising its third round in 12 months and the biggest ever in the sector in Europe. Brighteye Ventures’ analysis showed that VC investments in European edtech had breached $1 billion in a calendar year for the first time, even without GoStudent’s mega-round, with six months left to go.
Edtech deal flow in 2021 looks set to match or even outpace 2020 levels, per the report: At $9.4 million, average deal size is triple 2020 levels; seven companies have raised $50 million in five different markets; and the U.K. has more than three times as many deals as the next individual market.
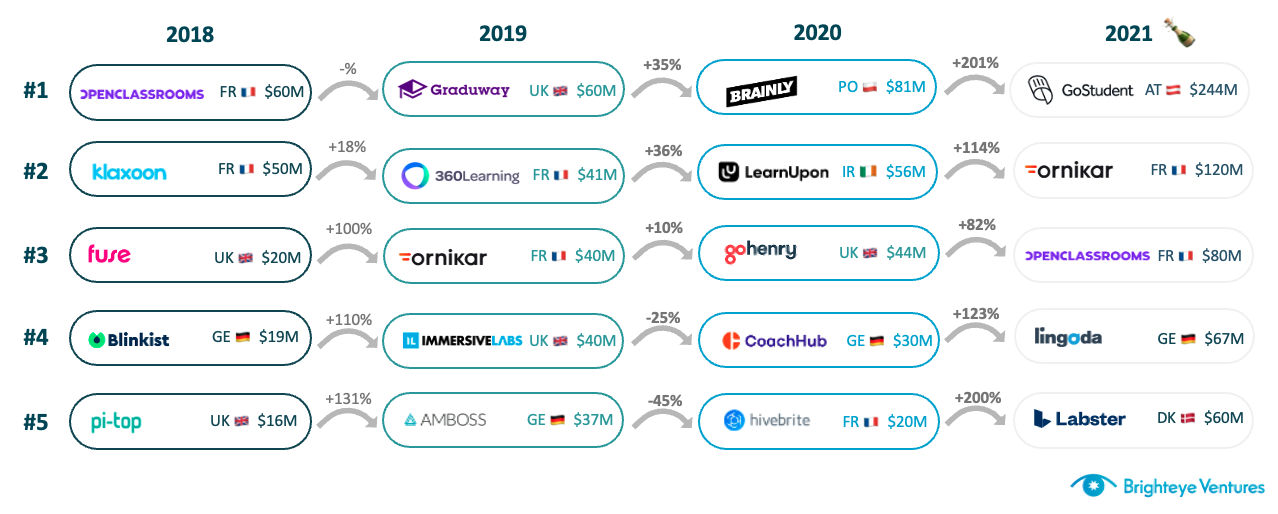
Deal-size progression in edtech over the years. Image Credits: Brighteye Ventures
It’s interesting that we are not seeing enormous increases in deal count. The $1.05-billion mark in the report is spread across 111 transactions — there were 237 in 2020, so we could expect a similar total this year. More funding and stable deal count of course means that we are seeing significant increases in deal size.
It seems generalist investors are recognizing that edtech investments can reap outsized returns, similar to sectors like deep tech, health tech and fintech.
We can draw a few conclusions from this. We can construe that companies created last year and in previous years matured significantly during the pandemic due to increased demand. Moreover, this rapid natural selection process provided insights on verticals and possible winners.
Lastly, it seems generalist investors are recognizing that edtech investments can reap outsized returns, similar to sectors like deep tech, health tech and fintech.
This is contributing to larger early rounds than we have seen in previous years — investors can’t pick the winner, but they can slant the playing field instead. We therefore expect to see a surge in the number of pre-seed, seed and Series A rounds in the second half of 2021, as companies founded during the pandemic begin to raise meaningful funding.
Another reason that edtech is being taken seriously by generalist investors is that the true size of the market (and the extent of digitization to come) is becoming more conceivable.
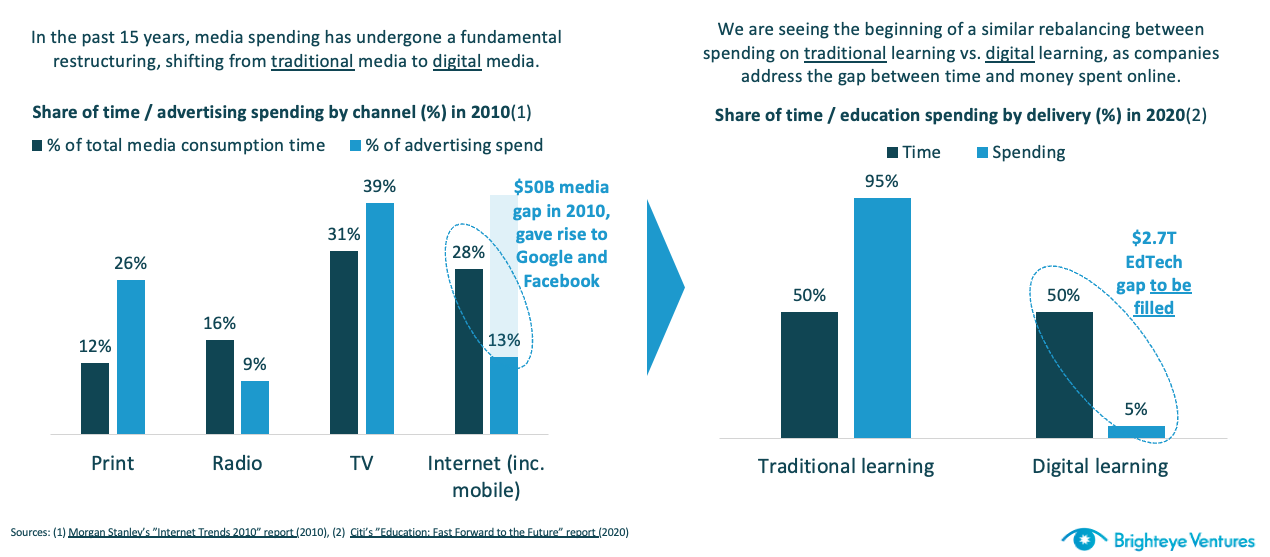
Edtech spending is growing like media spending did in the 2010s. Image Credits: Brighteye Ventures
Let’s work through a (very crude) market sizing example: Higher education in the U.K. In 2018/19, according to Universities UK, there were 2.38 million students studying at higher education institutions. We should acknowledge that in the context of Europe, the U.K. is a relatively large market with relatively high university participation.
Assuming all these students are full time (they’re not, some are part time and pay lower annual fees) and domestic (they’re not, some are international students and pay more than domestic students), at £9,000 each per year (~$12,502), these students are paying a total of £21.42 billion ($29.75 billion) to U.K. universities in fees alone.
This excludes living and materials expenses. In the U.K., a large portion of the fees used to be subsidized by the government to encourage higher participation in universities. A consequence of the fee change in the U.K. is that it feels like a far larger individual investment than it was in the past, regardless of the repayment mechanism and term. Fees aside, some would argue that the case for going to university is weakening, given that three years is quite a long time to study something that doesn’t necessarily lead to a particular career, guarantee a job, or provide a serious means of differentiating yourself from other candidates.
These four issues — cost, unclear career path, no job guarantee and low differentiation — are giving rise to a wave of edtech and learning tech companies offering more choice with shorter, cheaper, more career-oriented courses. The U.K. education market (for people aged 18-25) is, of course, far larger than £21.42 billion, given non-university vocational and technical routes, apprenticeships and other parts of the existing training market.
However, rigidities in the existing university system explain why there is so much edtech activity in 18-25+ education and training. This example is useful for another reason: It demonstrates that edtech markets in individual countries are enormous, let alone if companies can cross borders and capture market share in other countries.
The pandemic has tipped an already teetering sector toward an avalanche of digitization. We can no longer pretend that technology doesn’t enhance the way we learn, the education’s effectiveness or reduce the cost. It’s for these and other reasons that digitization presents an interesting set of challenges for policymakers. Governments and civil services don’t tend to manage, direct or deliver innovation, and they rarely own it once it’s developed.
We are therefore seeing a wave of private companies sweeping across parts of education and training that were overseen or funded centrally by governments. This is happening all across the world, but particularly in high- and middle-income countries. Policymakers are racing to create an environment and set of nudges that help individuals make the right choices within this new context.
The figures we reported last week reflect that investor groups, both in Europe and beyond, are recognizing that European edtech is maturing, and quickly. The fact that many generalist funds, including some large, globally renowned funds, are choosing to invest in European edtech is telling.
Investors can tell you that it was a unique opportunity and value proposition, but that should be taken with a truckload of salt. As TechCrunch’s viral article implies, investors love to pour cold water on anything they don’t consider appealing and shower all their decisions with praise. As more and more generalists invest in European edtech, across the continent, I think we will be hearing more praise for the sector.
You can read the half-year report here.
Disclaimer: Ornikar is a Brighteyes Ventures portfolio company.
