You know what tech startups hate? Complicated legal compliance. The problem is, Facebook isn’t a startup any more, but its competitors are.
There have been plenty of calls from congress and critics to regulate Facebook following the election interference scandal and now the Cambridge Analytica debacle. The government could require extensive ads transparency reporting or data privacy protections. That could cost Facebook a lot of money, slow down its operations, or inhibit its ability to build new products.
But the danger is that those same requirements could be much more onerous for a tiny upstart company to uphold. Without much cash or enough employees, and with product-market fit still to nail down, young startups might be anchored by the weight of regulation. It could prevent them from ever rising to become a true alternative to Facebook. Venture capitalists choosing whether to fund the next Facebook killer might look at the regulations as too high of a price of entry.

STANFORD, CA – JUNE 24: Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg (R) hugs U.S. President Barack Obama during the 2016 Global Entrepeneurship Summit at Stanford University on June 24, 2016 in Stanford, California. President Obama joined Silicon Valley leaders on the final day of the Global Entrepreneurship Summit. (Photo by Justin Sullivan/Getty Images)
The lack of viable alternatives has made the #DeleteFacebook movement toothless. Where are people going to go? Instagram? WhatsApp? The government already missed its chances to stop Facebook from acquiring these companies that are massive social networks in their own right.
The only social networks to carve out communities since Facebook’s rise did so largely by being completely different, like the ephemeral Snapchat that purposefully doesn’t serve as a web identity platform, and the mostly-public Twitter that caters to thought leaders and celebrities more than normal people sharing their personal lives. Blockchain-based decentralized social networks sound nice but may be impossible to spin up.
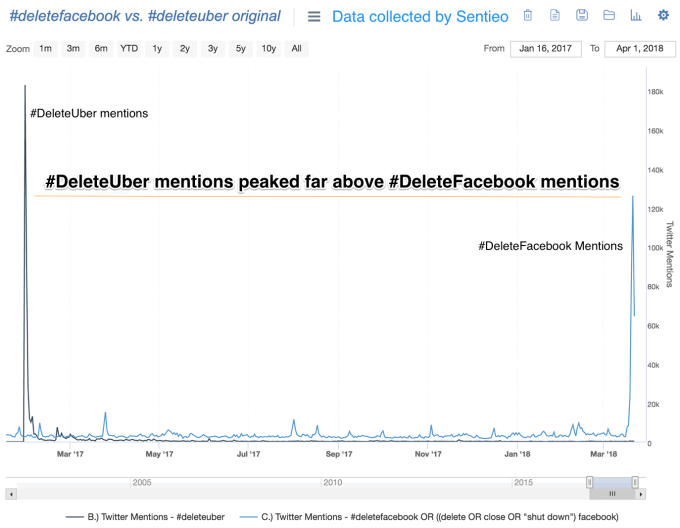
That’s left few places for Facebook haters to migrate. This might explain why despite having so many more users, #DeleteFacebook peaked last week at substantially fewer Twitter mentions than the big #DeleteUber campaign from last January, according to financial data dashboard Sentieo. Lyft’s existence makes #DeleteUber a tenable stance, because you don’t have to change your behavior pattern, just your brand of choice.
If the government actually wants to protect the public against Facebook abusing its power, it would need to go harder than the Honest Ads Act that would put political advertising on Internet platforms under the same scrutiny regarding disclosure of buyers as the rules for TV and radio advertising. That’s basically just extra paperwork for Facebook. We’ve seen regulatory expenses deter competition amongst broadband internet service providers and in other industries. Real change would necessitate regulation that either creates alternatives to Facebook or at least doesn’t inhibit their creation.
That could mean only requiring certain transparency and privacy protections from apps over a certain size, like 200 million daily users. This would put the cap a bit above Twitter and Snapchat’s size today, giving them time to prepare for compliance, while immediately regulating Facebook, Messenger, Instagram, WhatsApp, and Google’s social problem child YouTube.
Still, with Facebook earning billions in profit per quarter and a massive war chest built up, Mark Zuckerberg could effectively pay his way out of the problem. That’s why it makes perfect sense for him to have told CNN “I’m not sure we shouldn’t be regulated” and that “There are things like ad transparency regulation that I would love to see.” Particular regulatory hurdles amount to just tiny speed bumps for Facebook. Courting this level of regulation could bat down the question of whether it should be broken up or its News Feed algorithm needs to change.
Meanwhile, if the government instituted new rules for tech platforms collecting persona information going forward, it could effectively lock in Facebook’s lead in the data race. If it becomes more cumbersome to gather this kind of data, no competitor might ever amass an index of psychographic profiles and social graphs able to rival Facebook’s.

A much more consequential approach would be to break up Facebook, Instagram, and WhatsApp. Facebook is trying to preempt these drastic measures with Zuckerberg’s recent apology tour and its purchase of full-page ads in nine newspapers today claiming it understands its responsibility.
Establishing them as truly independent companies that compete would create meaningful alternatives to Facebook. Instagram and WhatsApp would have to concern themselves with actually becoming sustainable businesses. They’d all lose some economies of data scale, forfeiting the ability to share engineering, anti-spam, localization, ad sales, and other resources that a source close to Instagram told me it gained by being acquired in 2012, and that Facebook later applied to WhatsApp too.
Both permanent photo sharing and messaging would become two-horse races again. That could lead to the consumer-benefiting competition and innovation the government hopes for from regulation.
Yet with strong regulation like dismantling Facebook seeming beyond the resolve of congress, and weak regulation potentially protecting Facebook, perhaps it’s losing the moral high ground that will be Facebook’s real punishment.

Facebook chief legal officer Colin Stretch testifies before congress regarding Russian election interference
We’ve already seen that first-time download rates aren’t plummeting for Facebook, its App Store ranking has actually increased since the Cambridge Analytica scandal broke, and blue chip advertisers aren’t bailing, according to BuzzFeed. But Facebook relies on the perception of its benevolent mission to recruit top talent in Silicon Valley and beyond.
Techies take the job because they wake up each day believing that they’re having a massive positive influence by connecting the world. These people could have founded or worked at a new startup where they’d have discernible input on the direction of the product, and a chance to earn huge return multiples on their stock. Many have historically worked at Facebook because its ads say it’s the “Best place to build and make an impact”.
But if workers start to see that impact as negative, they might not enlist. This is what could achieve that which surface-level regulation can’t. It’s perhaps the most important repercussion of all the backlash about fake news, election interference, well-being, and data privacy: that losing talent could lead to a slow-down of innovation at Facebook that might leave the door open for a new challenger.
For more on Facebook’s Cambridge Analytica scandal, read our feature pieces:
