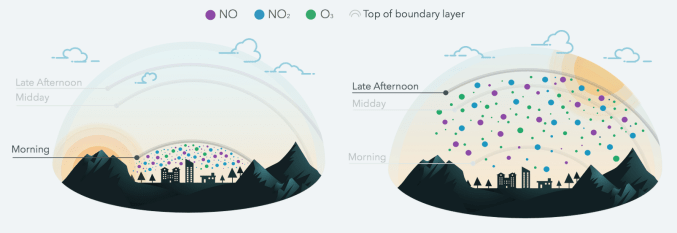
If a city knows what intersections are full of smog, it could add trees or change stop light schedules to improve the air its citizens breathe. Google Earth’s Outreach program that equips nonprofits and public-benefit organizations with data wants to give the world these insights.
So today, Google revealed that it’s been working with SF startup Aclima for the last year-and-a-half to attach air-quality sensors to its Street View cars.
“We designed our cities without data,” Aclima founder Davida Herzl tells me. Literally piggybacking on Google could let Aclima produce the data necessary to make urban areas easier on the lungs.
Testing the Aclima sensor
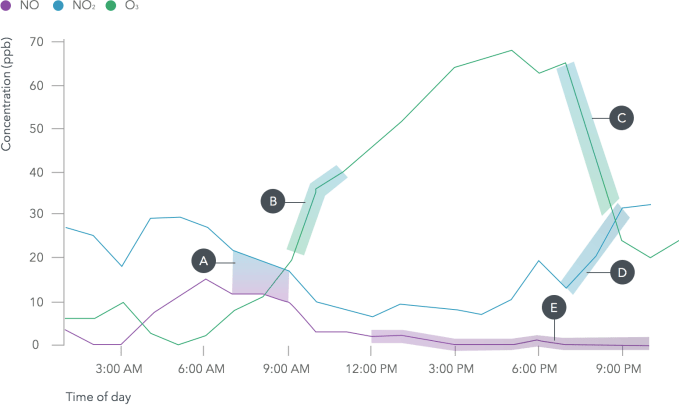
In the first pilot, three Street View cars collected 150 million air quality data points over a month of driving around Denver, Colo. They measured for chemicals that are hazardous to breathe, like nitrogen dioxide, nitric oxide, ozone, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane, black carbon, particulate matter, and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs).
The goal is to make data like this available to citizens so they and their local governments can see pollution on their own streets.
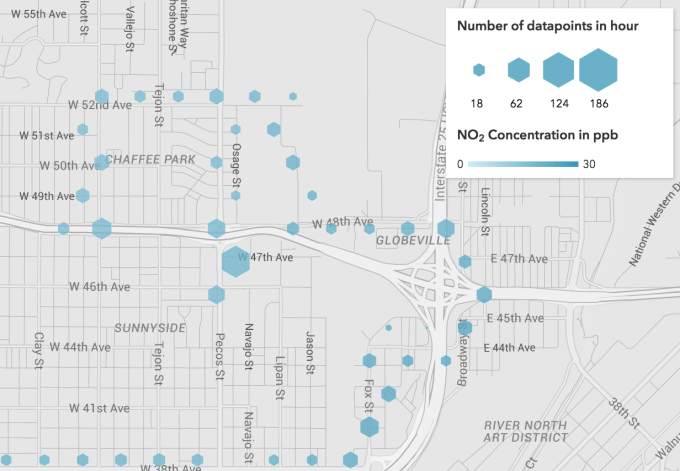
Independent scientific analysis confirmed that the mobile sensor system worked for collecting street-by-street data and could improve upon the regional network of sensors operated by the Environmental Protection Agency. Herzl says “we hope that one day this information is as accessible as the weather.” Here’s a video on how the program works:
Google has now agreed to purchase more of Aclima’s outdoor sensors for a bigger rollout to map air quality. Aclima-equipped Street View cars will criss-cross the Bay Area and other cities this year as part of the next big data collection.
The bootstrapped Aclima came out of stealth last month, detailing how it designs and builds its own sensors, manages the network as they collect data, processes the data on its cloud backend, and produces analytics and visualizations.
 The first project it announced was using indoor sensors to help Google measure air quality in its offices to optimize productivity.
The first project it announced was using indoor sensors to help Google measure air quality in its offices to optimize productivity.
For example, by tracking conference rooms throughout the day, Google could determine if CO2 levels climbed high enough to degrade brain function. If you’ve ever felt suffocated in a cramped meeting, you’re not crazy. With productivity of its huge elite workforce translating into billions in earned or lost revenue for Google, it has plenty of incentive to join up with Aclima.
For now, its Street View partnership is more charitable. Google Earth Outreach will help organizations use the data to visualize air-quality problems in cities, which could help them make arguments for fixes to city planners.
Herzl explains that “We know that trees absorb pollution, NO2 specifically. If we can know where pollution hotspots are, we can know where to put green spaces.” The Google partnership will allow it to rapidly scale the deployment of its sensors. This way, Aclima can pursue its mission to make a business out of improving human health through environmental protection.

There’s plenty more Google could potentially do with the data, though. It could allow Google Maps to route cars or pedestrians away from high-pollution areas to avoid exacerbating condensed pollution or breathing it in.
The ability to direct self-driving cars away from intersections where they might contribute to high-pollution zones could help convince cities they’re a positive change. I’ve asked Google for a comment on these possibilities and am waiting to hear back.
Herzl concludes that Aclima’s sensors are producing social good out of the Internet Of Things, which is often thought of as just equipping homes with Wi-Fi-connected appliances. She tells me, “There’s a whole new world of opportunities to make our cities healthier, not just smarter.”