One of the early pioneers in the Quantified Self movement has quietly gone out of business. Zeo, a leading maker of hardware and software used by consumers to track sleep and improve their health, has not been operating since the end of last year. A trustee has nearly completed the sale of all company assets. Zeo has been very quiet about the news up until now. In fact, Zeo’s website is still up and doesn’t mention the news.
Zeo was founded by three students at Brown University who had a passion for using the science of sleep and technology to improve people’s lives. The company introduced its first product, the Zeo Personal Sleep Coach, in June 2009.
The following week, the first article mentioning the term “Quantified Self” was published in Wired magazine. While the article didn’t mention Zeo, it did claim “a new culture of personal data was taking shape.” And that every facet of life from sleep to mood to pain was becoming trackable. “Even sleep – a challenge to self-track, obviously, since you’re unconscious – is yielding to the skill of the widget maker.”
In 2011, the widget maker Zeo introduced a mobile version to its Sleep Manager product line. By wearing a special headband, with sensors to measure electrical current, the Zeo could track different phases of sleep, such as Light, Deep and REM sleep, in addition to awake time. This data was then sent to an iPhone, iPod, or Android phone, and could be automatically uploaded to a personal and private online sleep database. This data along with some analytical tools could then be used to help improve your sleep and health.
What Went Wrong
Former CEO, Dave Dickinson, who lead the company for the past 5 years, tells TechCrunch the problem was not the brand or the product. In fact, the company was growing before it shut down.
Dickinson says the problem was the business model. “The business model is more important than the brand. Consumer health devices are a very capital-intensive business. You have to find enough money to address the consumer, funds to address the physicians, and also the retailers, and that’s up and above the device business having to fund inventory.”
Zeo had two business model options on the revenue side. Become a SAAS-like business with subscriptions and recurring revenue or make enough money from a customer who bought just one unit. But that was very difficult when the company started pricing its mobile product at $99, with ‘sub-optimal’ profit margins.
The Newton, Massachusetts-based company had raised more than $30 million over eight years. Dickinson says raising capital was not the problem.
Sleep Tracking As A Commodity
Another problem for Zeo was that sleep tracking became a commodity. Devices like the FitBit, lark, and Jawbone Up use an accelerometer to determine sleep and awake cycles, using wrist actigraphy. These products brand their products as sleep trackers just like Zeo.
Dickinson says Zeo had peer-reviewed scientific studies, including one published in the Journal of Sleep Research, showing his technology was 7/8th as accurate as data from the a sleep lab, considered to be the gold standard for measuring sleep. The study also says data from wrist actigraphy to measure tiny motions in devices are much less accurate. But that didn’t seem to matter for enough consumers.
The Competition
Dickinson says he admires what the Fitbit and others like it have done. Those devices are not limited to one health issue like sleep, which was another problem for Zeo. Those other products work for different health and wellness areas, such as the well established desire to lose weight and become physically fit. Consumers already spend billions of dollars to achieve those goals. And they are already educated and motivated to improve their weight and fitness.
Part of Zeo’s business model required it to educate the consumer on the importance of sleep and how sleep awareness and data can improve your health. Arianna Huffington, Editor-in-Chief of the Huffington Post, our AOL sister site, has been a crusader on the importance of sleep to your health. But according to Dickinson, “sleep is still lagging behind as important to your wellness. So in that respect, Zeo was early in terms of its mission.”
The Product
I used the device for several months last year and thought it was amazing. While wearing the headband took some getting used to, for me and my wife, the data it revealed was eye-popping. In addition to learning that I wasn’t getting enough sleep, which I knew already, I learned about the different types of sleep I was getting.
Most nights, I would get a half hour to an hour of “Deep Sleep” (dark green in the chart below) after going to bed. This is the phase of sleep the helps you feel restored and refreshed.
I would also see several periods of REM sleep, important for overall mental health, mood, and the ability to retain knowledge. The bulk of my time asleep, like most people, was spent in “Light Sleep,” which is better than not sleeping but doesn’t do as much for my health as Deep or REM sleep.
I was able to see graphics like this on my iPhone in the morning.
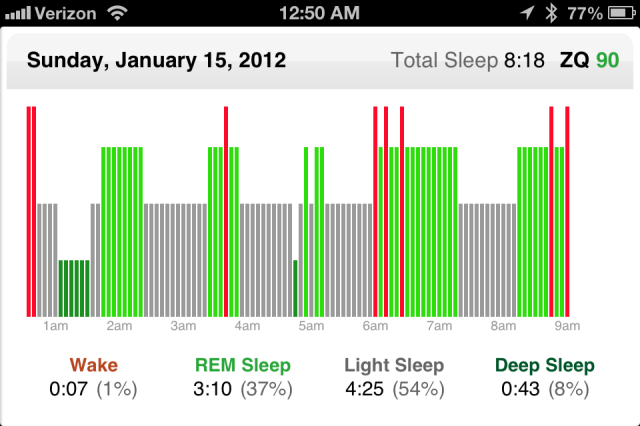
Here’s a good night with a sleep score of 90 out of 100 and more than 8 hours of sleep.
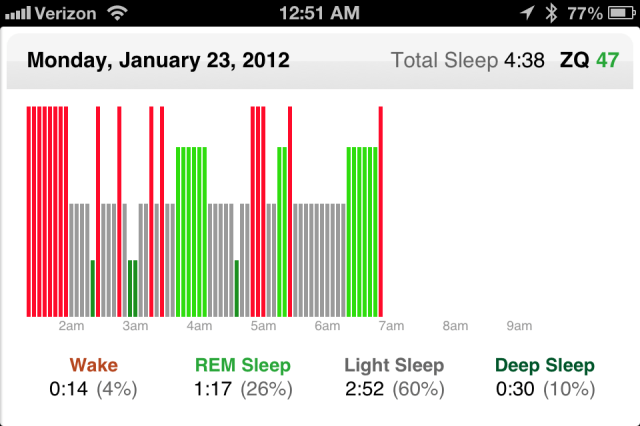
And here’s a bad night, with a score of 47 with just 4 and a half hours of total sleep.
If I woke up in the morning during REM sleep, it was hard to get out of bed. If I didn’t get enough Deep Sleep, I didn’t feel I had a good night sleep.
Zeo claimed the real value of the program was I could get personalized online sleep coaching. But this required logging in to the website and entering more information about my sleep and other variables I wanted to track. If I could have entered the data right on my iPhone, I would have likely used it more. Since it required logging in on the website, it proved too much friction for me.
I also stopped wearing the headband after a while because it does feel a bit awkward. The former CEO says the company was aware the device was too invasive for some customers.
But if a less invasive sensor was made and it was easier to enter custom data and get actionable information, I would have used it every night.
What’s Next
Dickinson can’t comment on exactly what’s next for Zeo, after all the assets are sold. But he is hopeful that there may be an opportunity for the company to re-emerge in the future.
An article appeared in the MobiHealthNews in March, that reported the Better Business Bureau had listed Zeo as being “out of business” but with no official announcement by the company, the news hasn’t been widely known.
It is still possible to log-in to Zeo’s “My Sleep” site that contains your sleep data. An article on the Quantified Self website today tells users how they can download their data in case the site goes offline.
As word about Zeo’s status has spread, Dickinson says they have received tremendous support and inquires from all over the world from disappointed customers and sleep researchers who had planned to use the units for the research.
He wrote a post on the MobiHealthNews site last week that included some additional lessons learned. He concluded by writing “motivating behavioral change through data visualization can be very powerful, but it is more of an art than a science. We will need far more artists, user interface experts and psychologists to help make our data work harder to motivate better health.”