Spotify’s decision to lay off 17% of its staff is the leading technology story of the morning, and I wouldn’t fault you if you were a little confused why it is doing so. After all, the music streaming company just reported positive operating income and nine figures’ worth of free cash flow in the third quarter.
Well, the short answer is: Corporate and market fundamentals.
Spotify has grown into a truly massive company. In the third quarter, its revenue rose 11% to €3.36 billion from a year ago, which put it on a roughly €13.4 billion run rate. That’s a lot.
But even though the company is raking in revenue and profit (last year it reported an operating loss and far-slimmer free cash flow), it isn’t getting the sort of respect from investors that it once enjoyed. It’s likely Spotify wants to earn that respect again.
Here’s a chart showing Spotify’s price-sales ratio, a trailing metric that is the grown-up version of the revenue multiple standard that we tend to use for startups:
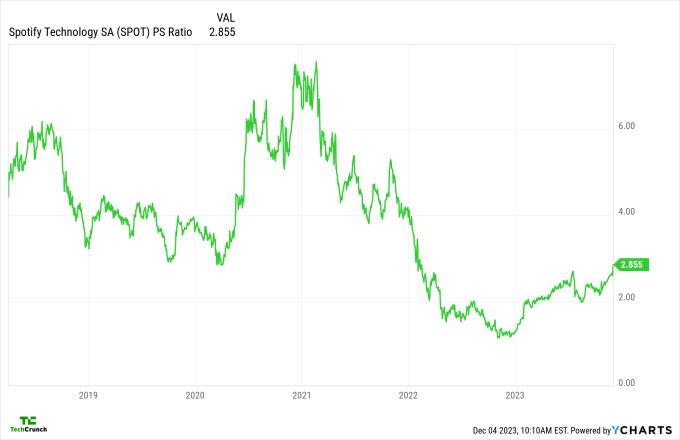
Image Credits: YCharts
The chart tells us two things:
- Spotify was once awarded a far better multiple on its revenue than it enjoys today.
- The company’s price-sales ratio has recovered from the lows it reached in late 2022 and early 2023.
The company wants more. How could Spotify argue with investors that it deserves a richer valuation? It could:
- Accelerate revenue growth: If Spotify could boost revenue growth, its value would rise thanks to the implied gains in the expected value of its future cash flows.
- Improve revenue quality: If Spotify could bolster its gross margins, it could generate more profitable revenue. Again, this would improve its long-term economics and therefore its value.
- Drive profitability through cost cuts: Spotify could cut its expenses and become more profitable, and thus more valuable, without making any changes to the pace of its revenue growth or revenue quality.
Spotify may be able to find a few extra points of revenue growth in the coming quarters and years. It’s working on its advertising-based product, it is still a big name in podcasts, and has some consumer pricing flexibility. But those facts have been true for a while now, so expecting Spotify to suddenly outgrow its core market (music) is going to be tough.
For reference, global music revenue increased between 6.7% and 9% in 2022, and it’s set to rise at a similar pace this year, too. Even if you consider Spotify to be a leading driver of music sales, it can only outpace the music industry’s GDP by so much. It’s unlikely the company can augment its top line fast enough to earn a stronger revenue multiple.
Revenue quality is another stuck issue. Spotify has shown some progress here, but its gross margins have been hovering around the mid-20s point for more than a year now — 24.7% in Q3 2022, 24.1% in Q2 2023, and 26.4% in Q3 2023. Can the company stretch that metric to 30%? Spotify’s core product is not its own, since it doesn’t own the music that it streams, so it’s tough to predict that. But given that the company has had massive market share, clout and industry investment for a long time and is still stuck around 25%, I would hazard that a step-change is not coming.
So, what’s left? Cost cuts, which explains the significant layoffs. Here’s how Spotify described the near-term impacts of the cuts to the SEC:
The Company estimates that it will incur approximately €130–145 million in charges in the fourth fiscal quarter of 2023, primarily consisting of severance-related payments and the impairment of real estate assets as a part of optimizing the Company’s office space footprint in connection with the reduction in the employee base, partially offset by forfeitures of equity awards by departing employees. The majority of the cash component of these charges will occur over the first and second fiscal quarters of 2024. The Company anticipates that these actions will generate meaningful operating efficiencies going forward.
Due to the charges noted above, the Company is updating its Operating Income/(Loss) outlook for the fourth fiscal quarter of 2023 to a range of €(93)–€(108) million.
So, near-term costs and long-term “meaningful operating efficiencies.” That model fits neatly with our theory of the company boosting its profitability through cost reductions.
You have to discard startup thinking to understand what Spotify is doing. The company is not fighting for life; it is default alive. It is simply tinkering with its economics so that it is more attractive to investors. That means it needs to pay fewer salaries.
A good day for tech workers? Hell no. A lot of people are going to take home severance for Christmas instead of work plans for the new year. That’s brutal.
In human terms, these layoffs are wild. It feels like an incredibly callous move for a profitable company to let staff go because it wants to be more profitable. But what other choice did Spotify have if it wanted to bump its price-sales ratio above 3x?
(Note: In a fit of the Mondays, I initially reported Spotify’s results in dollars, not euros. This has been corrected.)
