After the big companies conducted mega layoffs at the beginning of this year, it would be natural to think that the tech unemployment rate would skyrocket. If we think about tech jobs as purely IT, engineering and developer kinds of roles, then those jobs are definitely still in demand and less affected than you might imagine.
There’s a big factor working in the favor of tech professionals looking for work: They’re sought after in both the technology industry and across other industries that also require workers with the same technical skills. Those non-technology companies are finally getting a shot at some of the better talent that has been locked in tech industry jobs for the last few years.
Still, when you add tens of thousands of people to the unemployment payroll, it’s bound to have an impact eventually — even if all those jobs weren’t pure tech jobs.
Right after the latest jobs numbers came out earlier this month, the number of job openings across all sectors fell to its lowest level in two years. What’s more, CompTIA found that tech job posting volume was down, suggesting that companies might have put hiring on hold, at least for the short-term.
This hardly seems surprising, given that the Fed has been raising interest rates for the last 19 months with the specific goal of cooling the economy. In fact, over the last year, rates ballooned from 1.68% in July 2022 to over 5% today. The attempts seemed to have worked if the declining jobs data is any indication.
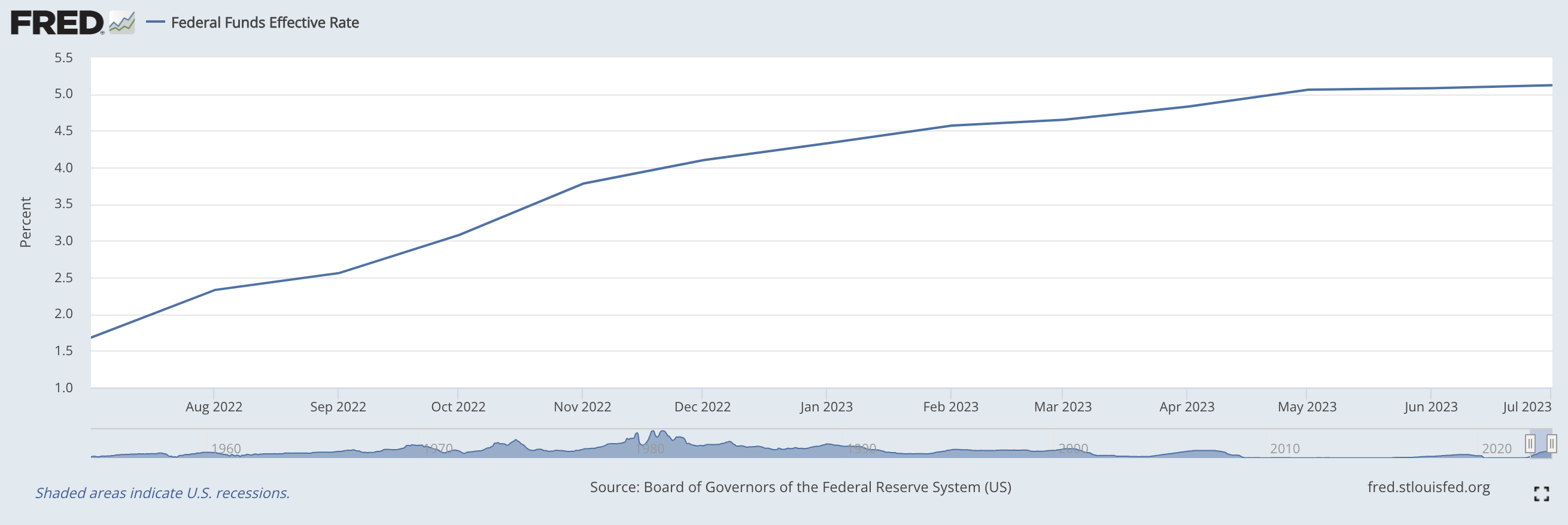
Fed interest rate hikes from July 2022 to July 2023 Image Credits: FRED
When we looked at the tech jobs outlook in February, we expected it to be worse than it was, but tech jobs growth remained surprisingly strong. Today, the picture isn’t quite as bright — though not awful — but there is clearly a shifting landscape for tech workers.
And you may ask yourself, “How did we get here?”
You may recall (or may have stricken it from your memory due to the trauma) that in March 2020, we went into a lockdown. That caused the economy and tech jobs to plunge briefly, but throughout that year and into 2021, companies began recognizing that there was a business opportunity in having so many workers at home.
Cloud stocks went through the roof, and tech companies hired and hired for what they believed was an incoming permanent change in the market. But it wasn’t. Using Microsoft as an example, here’s what we wrote at the time of the company’s announcement it would be laying off 10,000 people in January:
Consider that Microsoft had over 220,000 employees at the end of last year, according to Statista. That’s up from 163,000 in 2020 and 181,000 in 2021, meaning the company added more than 57,000 employees in a two-year period before cutting 10,000 this week.
When you look at the other Big Tech companies, it was a similar story, and by January 2023, 58,000 people from the world’s biggest tech companies were put on the streets, many of whom were the highly qualified tech workers we’re talking about in this article.
Now the companies could find themselves on the other side of that problem. Oops. They overcompensated yet again. The management at these companies seem to have made two glaring strategic errors in a very short time: first overhiring, then laying off too aggressively.
And some of these companies might pay a price for overcorrecting when the economy turns again, said Atta Tarki, founder and chairman of executive search and staffing firm ECA Partners and author of the book “Evidence-Based Recruiting.”
“For IT jobs, I suspect that there will be a crunch for talent in the market once the economy starts recovering,” he told TechCrunch+. “A lot of tech companies made deeper cuts than the general economy, anticipating a downturn. When the economy turns, they [could] scramble to find enough talent.”
And you may ask yourself, “Am I right? Am I wrong?”
Overall, though, the July jobs report was more than decent for a supposedly slowing economy. New jobs were still well in the positive territory at 209,000, and unemployment overall was 3.6%, numbers that would look good in any economy, never mind one being pounded by the Fed’s constant rate hikes.
CompTIA found that tech unemployment dropped below 2% this month after rising last month. Tim Herbert, chief research officer at CompTIA, says it’s hard to get a clear reading as the numbers have fluctuated so much from month to month. “What we’ve seen since the last time we spoke has been a pattern of monthly fluctuations. So it is a little bit interesting that we have seen these periods where the numbers will be strong one month, and then the follow up month, they’ll pretty much be weak across the board. And then the pattern reverses itself the following month,” Herbert told TechCrunch+. “So I think that’s the challenge that we’re still trying to take the net effect of some of these opposing forces.”

Tech unemployment rate is always much lower than the general rate. Source: CompTIA
The number of new digital jobs is still growing, although more slowly than last year. “For the third time this year, the net employment outlook is still very positive, 39%, an improvement of 5% . . . over last quarter, albeit weakening 7% against the same quarter last year — but still extremely positive,” said Ger Doyle, head of Experis at Manpower Group.
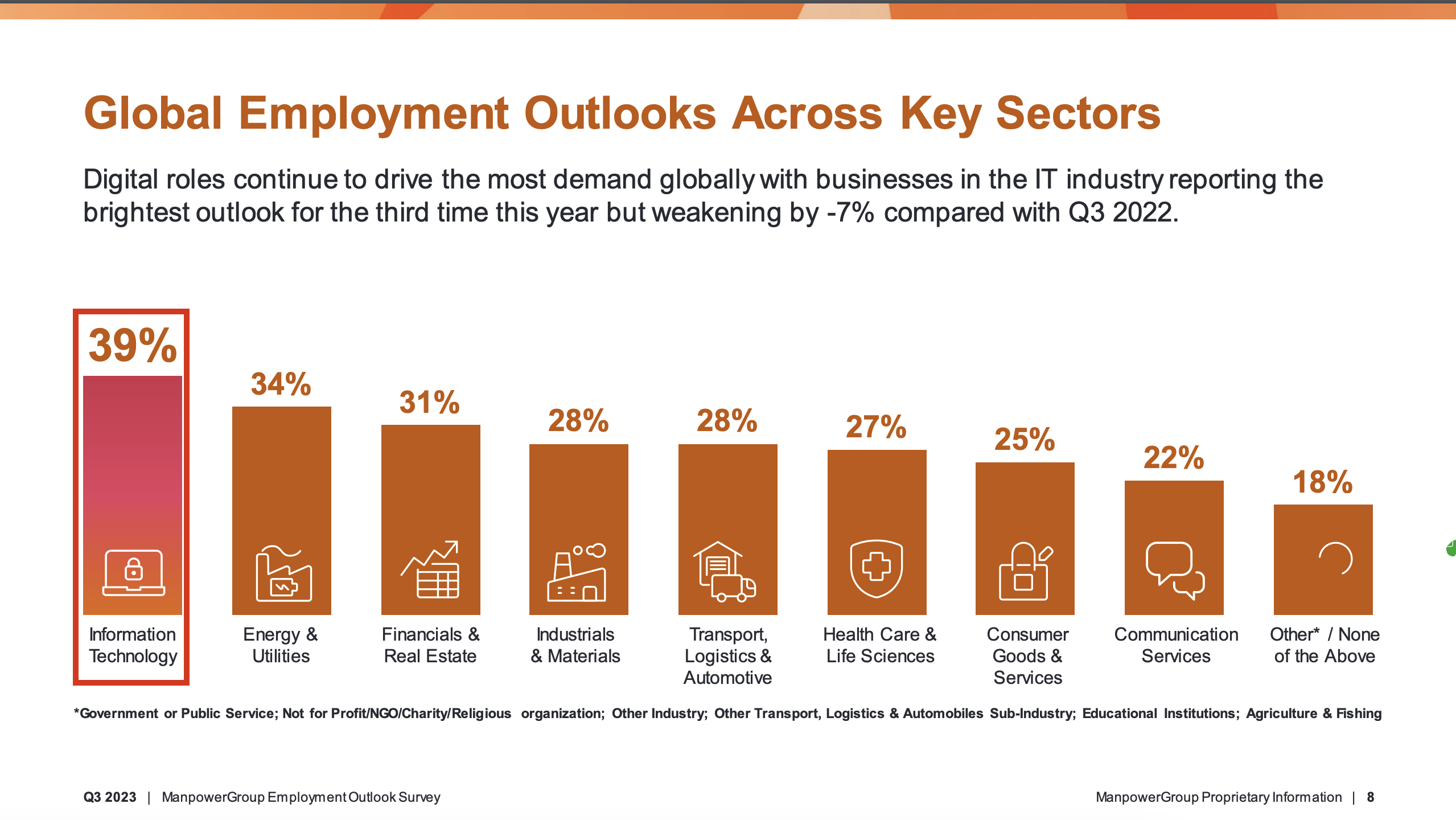
Image Credits: Manpower Group
In fact, as you can see from the chart, IT still remains the fastest-growing job category by a fair amount.
In spite of that, Tarki believes that we could see some short-term turbulence in the market before it begins to turn around. “My sense is that IT staffing firms will have a tough time for the next few months. However, one of the downsides of a soft landing overall is that the recovery is most likely going to be soft as well, meaning that there will not be a strong upswing like the one we experienced in 2021,” Tarki said.
Even though the fluctuating numbers make it hard to predict what’s happening, Herbert said that all of the long-term signs are still positive, both based on the monthly data as well as what his firm picks up in CIO surveys it conducts.
“Everyone continues to look at investments and see how tech will be an important component in their long-term growth strategy, but accounting for some of the monthly fluctuations is just always a tricky proposition,” he said.
