In the crypto world, there’s a popular maxim called the Blockchain Trilemma, which refers to the difficulty of simultaneously achieving three desirable properties in a blockchain network: security, scalability and decentralization.
The trilemma states that it is impossible to have all three properties at their maximum level. As a blockchain network becomes more secure, it becomes less scalable; as it becomes more scalable, it becomes less secure; and as it becomes more decentralized, it becomes less secure and less scalable.
When designing a blockchain system, trade-offs must be made among the three parameters, leading to a balance that is acceptable for a specific use case.
There is a similar trilemma that exists for on-demand delivery in the convenience foods sector:
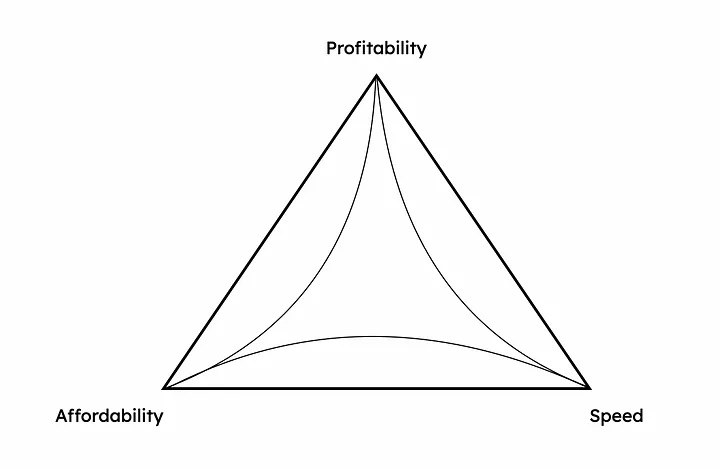
The “on-demand delivery trilemma.” Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
It refers to the challenge of balancing three of the most important factors in the on-demand delivery of convenience foods: speed, profitability and affordability.
With the model of delivering preordered goods, it is impossible to maximize all three factors at the same time.
This “on-demand delivery trilemma” will continue to plague industry incumbents unless they can think beyond the existing model of delivering preordered goods.
For example, to achieve low delivery costs to pass on to consumers, or in other words, achieve affordability, the delivery system has to sacrifice either profitability or speed. To be profitable, the company needs to charge high fees, making it unaffordable, or improve its cost basis by being slow. To be fast, the company either needs to be profitable, which means charging high fees, or forgo those fees and sacrifice profitability.
Below, I’ll provide examples of each of the trade-offs and why it is not possible to get around them when employing the existing model of delivering preordered goods.
Incumbents using this existing model of delivery include:
- Delivery robots.
- Route-based ice cream and food trucks.
- Delivery apps.
- Quick commerce.
Delivery robots
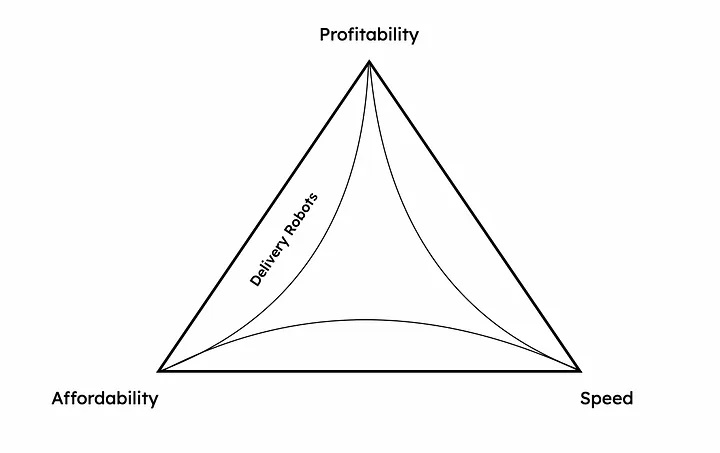
Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
Delivery robot companies like Starship, Nuro, Serve, Kiwi and Coco reduce costs by automating the driver. This reduction in cost helps them achieve profitability and affordability, but they sacrifice speed to do so.
It takes longer for a robot to deliver something than it would take a person, and considerably so when we’re talking about slow-moving sidewalk bots.
Route-based trucks
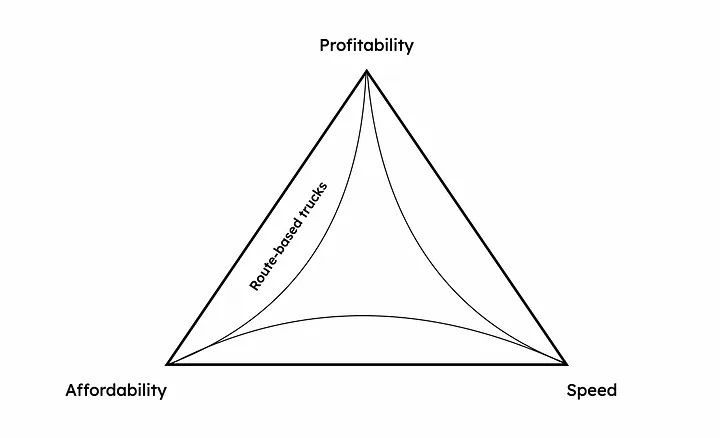
Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
Route-based ice cream and food trucks have existed for decades, but new companies like Scream Truck and Zing are trying to modernize them.
However, they operate on the same underlying model of preordering goods and so can achieve only profitability and affordability; not speed.
By virtue of being route based, they park in central locations and force consumers to come to them, line up and buy goods to either consume or haul back home. A considerably slow experience.
Delivery apps
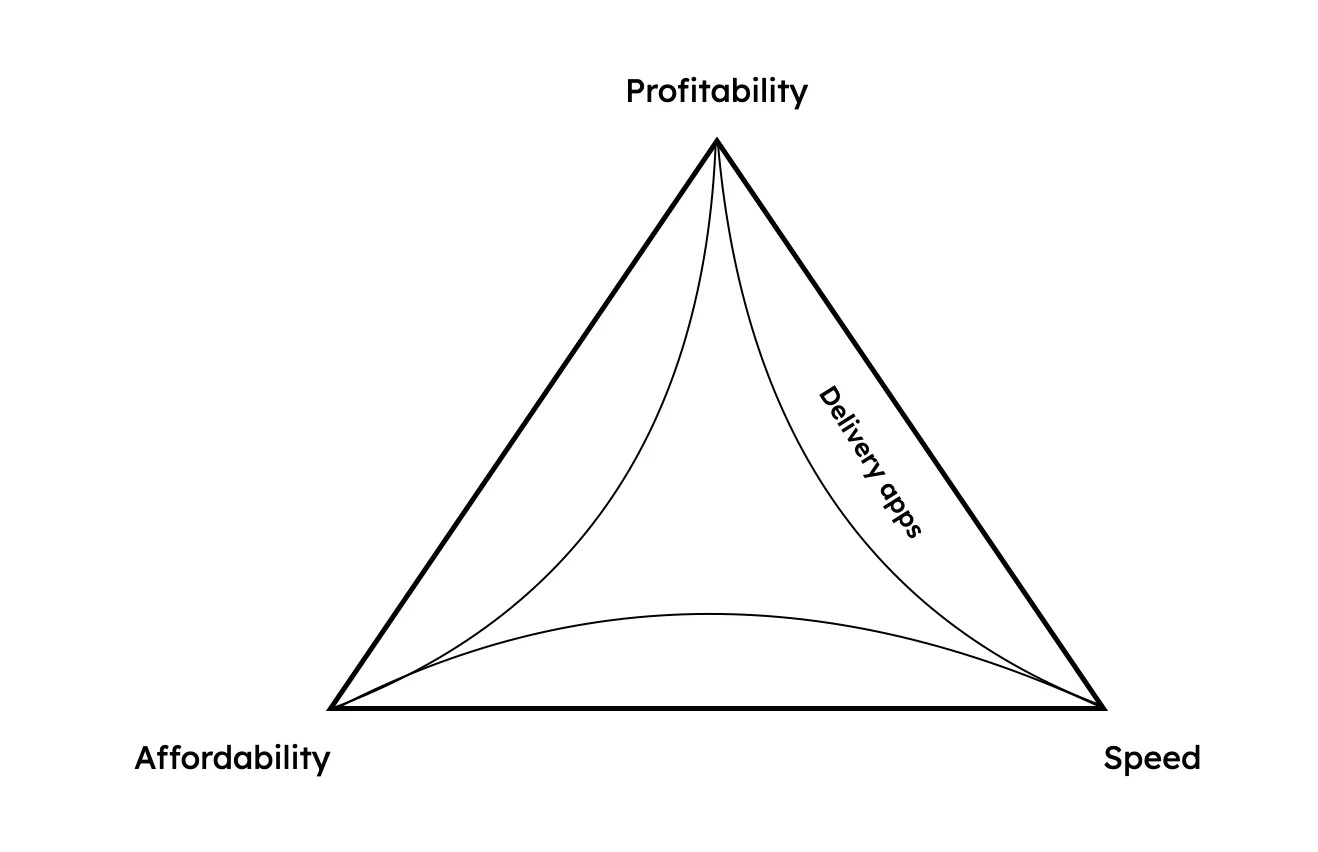
Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
On the right side of the trilemma, we have incumbent delivery apps like DoorDash and UberEats, which are fast and can be profitable.
The issue is that they can only be profitable at an extremely high cost. They pass on these costs to the consumer in the form of delivery fees, service charges and tips, all of which can easily be close to $10 per order.
Quick commerce
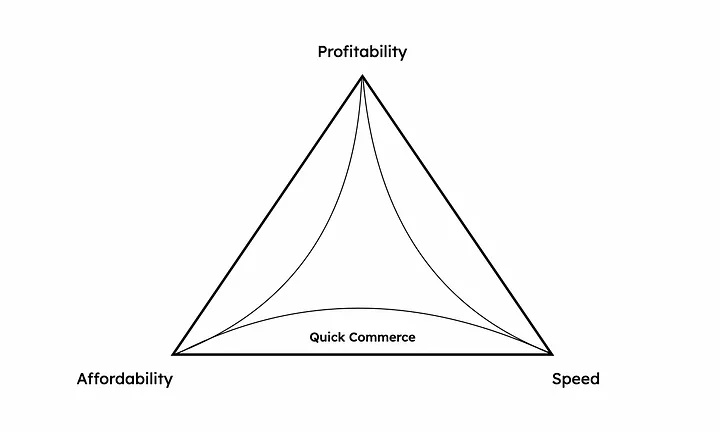
Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
Finally at the bottom of the trilemma, you have services that attain speed and affordability, like Getir, Gorillas (part of Getir), GoPuff and Flink. However, in their quest to deliver cheaply and quickly, they sacrifice profitability. On average, they manage up to three deliveries an hour at most, which means that no matter how fast or cheap they get, they won’t be able to break even.
There is, however, an emerging model that addresses and solves the trilemma and gets around its challenges. This model completely reimagines delivery of convenience foods and changes the model of delivering preordered goods.
Roving shops
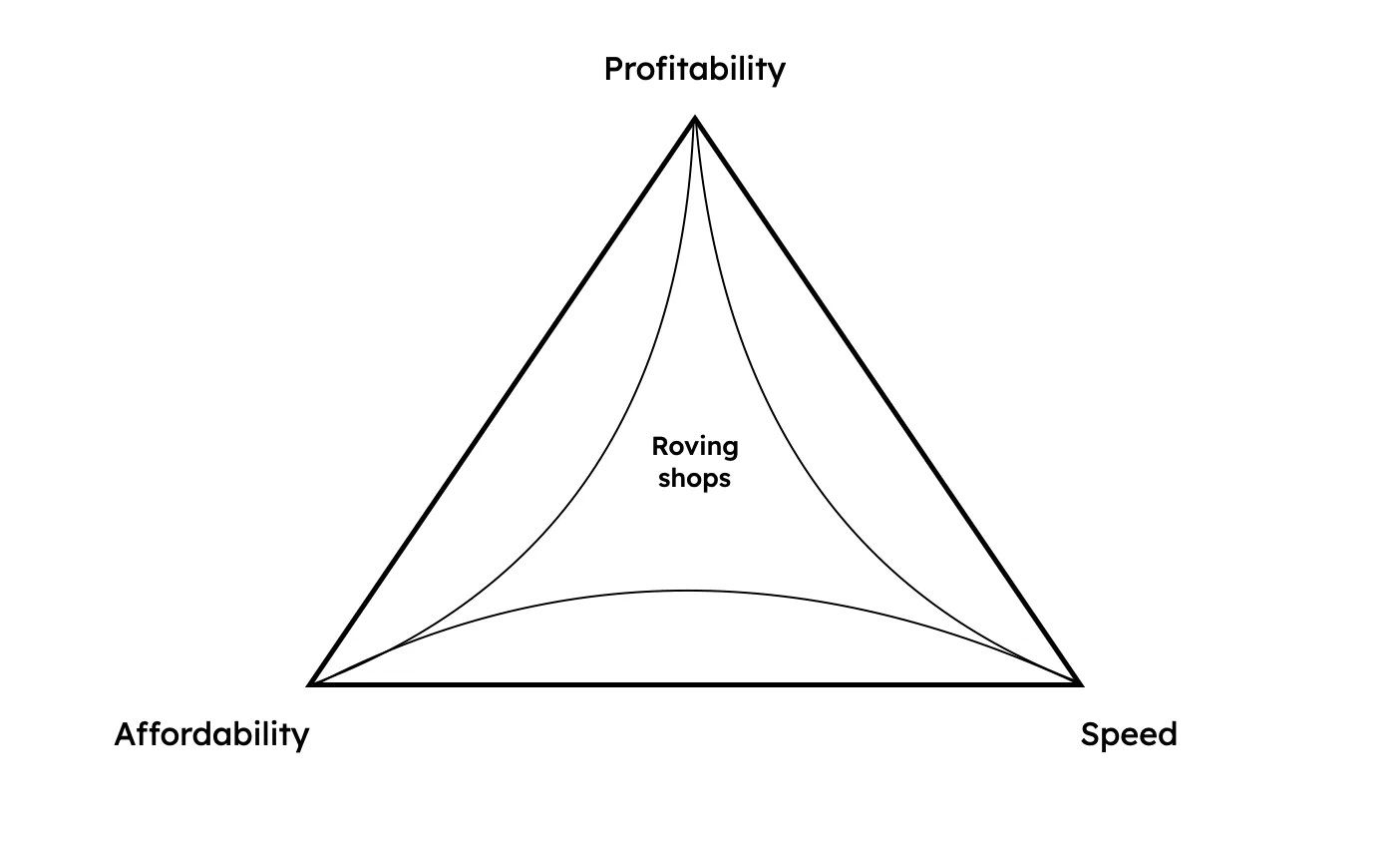
Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
Roving shops are on-demand food trucks, snack shops and ice cream shops that carry all their inventory within vans. They do not require order pickups and so can get around the trilemma to create a model that is fast, cheap and profitable.
Companies in this space include Conjure, my own startup, and Muncho, a pizza shop that parbakes pizzas and finishes them off in the van en route to the customer.
Both are able to manage about five orders per hour to achieve profitability, because they don’t need to pick up orders and can have their vans/shops driving in areas with potential demand. This means that not only is the model profitable, they can pass on the cost savings to consumers and ensure quick delivery.
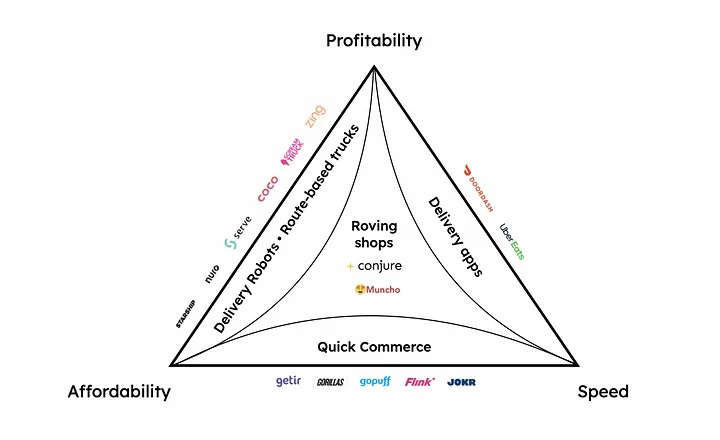
Image Credits: Ali Ahmed
Several companies have attempted this model in the past, like Zume Pizza and Wonder. Both pivoted away from the model because they spent a ton of capital trying a vertically integrated approach, which added significant costs.
The new crop of roving shops are taking an asset-light approach by using off-the-shelf equipment and rented vehicles to keep costs low. Additionally, algorithms that constantly match supply to demand ensure throughput of vehicles in any neighborhood they operate in.
This “on-demand delivery trilemma” will continue to plague industry incumbents unless they can think beyond the existing model of delivering preordered goods and find new, compelling ways to get goods to consumers in the fastest, cheapest and most profitable way possible.
