 IBM has purchased open source, cloud software business Red Hat for $34 billion in cash and debt. The deal sees IBM betting big on the cloud, specifically cloud services, that blend on-premises and cloud-based architectures. Red Hat will be a distinct unit within IBM’s Hybrid Cloud team, and it will continue to focus on open-source software. The acquisition is expected to close in the latter half of 2019.
IBM has purchased open source, cloud software business Red Hat for $34 billion in cash and debt. The deal sees IBM betting big on the cloud, specifically cloud services, that blend on-premises and cloud-based architectures. Red Hat will be a distinct unit within IBM’s Hybrid Cloud team, and it will continue to focus on open-source software. The acquisition is expected to close in the latter half of 2019.
Developing Story
IBM acquires Red Hat
Assessing IBM’s $34 billion Red Hat acquisition
As you look at the $34 billion IBM-Red Hat deal announced yesterday, if you follow the enterprise closely, it seems like a good move, at least on its face. It could be years before we understand the true value of it for IBM (or lack thereof, depending on how it ultimately goes). The questions stands then, is this a savvy move, a desperate one or perhaps a bit of both. It turns out, it depends on whom you ask.
For starters, there is the sheer amount of money involved, a 63 percent premium on Friday’s closing price of just under $117 a share. IBM spent $190 a share, but as Ray Wang, founder and chief analyst at Constellation Research said, Red Hat didn’t necessarily want to be sold, so IBM had to overpay to get their company.
Wang sees cloud, Linux and security as the big drivers on IBM’s part. “IBM is doubling down on the cloud, but they also are going for a grab in Linux for their largest and most important open source communities and some of the newer tech on Red Hat security,” he told TechCrunch. He acknowledges that it’s a huge premium for the stock, but he believes IBM needs the M&A action to drive down customer acquisition costs and drive up cross sell.

Photo: Ron Miller
IBM is placing a big bet here says Dharmesh Thakker, general partner at Battery Ventures, believing it to be worth 30x its current earnings in the next 12 months. “Needless to say, the hybrid cloud opportunity that we have been working on the last few years, is real and IBM/Cisco/HP/Dell all want a piece of this action going forward as the $300B in datacenter spend gets dislocated by public and hybrid cloud vendors,” Thakker explained in a statement.
He believes this deal could actually trigger a new set of mega mergers between the traditional tech vendors and cloud native, container and DevOps companies over the next few months.
IBM CEO Ginni Rometty was positively giddy at the prospects of a combined IBM-Red Hat in a call with analysts and press this morning, pointing out that only 20 percent of enterprise workloads have been moved to the cloud. She sees a big opportunity, one she projects to be worth $1 trillion by 2020. Keeping in mind you should take market projections with a grain of salt, this is undoubtedly a big market and one that Oracle and Microsoft have also targeted.
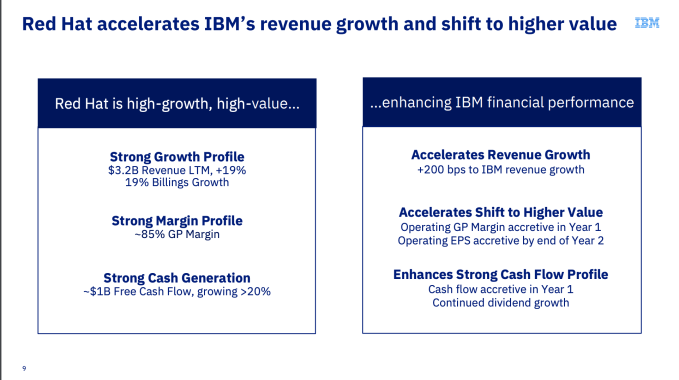
She said that Red Hat was a rare company indeed. “Red Hat on its own has been a high value company and has done a great job with strong growth, is highly profitable and generates cash. There are not many companies out there that look like that in this area,” Rometty said.
Slide: IBM
Dan Scholnick, general partner at Trinity Ventures, whose investments have included New Relic and Docker, was not terribly impressed with the deal, believing it smacked of desperation on IBM’s part.
“IBM is a declining business that somehow needs to become relevant in the cloud era. Red Hat is not the answer. Red Hat’s business centers around an operating system, which is a layer of the technology stack that has been completely commoditized by cloud. (If you use AWS, you can get Amazon’s OS for free, so why would you pay Red Hat?) Red Hat has NO story for cloud,” he claimed in a statement.
That might not be an entirely fair assessment. While Red Hat Enterprise Linux is a big part of the company’s revenue, it’s not the only piece. Over the last couple of years it has moved into Kubernetes and containerization and has grown the cloud native side of the business alongside RHEL.
In fact, Forrester analyst Dave Bartoletti sees the cloud native piece as being key here. “The combined company has a leading Kubernetes and container-based cloud-native development platform, and a much broader open source middleware and developer tools portfolio than either company separately. While any acquisition of this size will take time to play out, the combined company will be sure to reshape the open source and cloud platforms market for years to come,” he said.
Photo: IBM
Wang believes the deal could hinge on how long Red Hat CEO Jim Whitehurst, who had led the company for over a decade, stays with the unit. According to IBM, they will maintain the Red Hat brand and operate it as an independent entity inside Big Blue. “If Whitehurst doesn’t stick around for awhile, the deal could go south,” he said. But the company could dangle the CEO job when Rometty decides to leave as incentive to stay.
Regardless, Wall Street was not entirely happy with IBM’s move with their stock down all day. Needless to say the 63 percent premium IBM paid for the stock has driven Red Hat higher today.
The deal must pass shareholder muster, but given the premium IBM has offered, it’s hard to believe they would turn it down. In addition, since these companies operate across the world, they are subject to the global regulatory approval process. They won’t officially come together until at least the second half of next year at the soonest. That’s when we might begin to learn whether this was a brilliant or desperate move by IBM.
IBM is betting the farm on Red Hat, and it better not mess up
Who expects a $34 billion deal involving two enterprise powerhouses to drop on a Sunday afternoon, but IBM and Red Hat surprised us yesterday when they pulled the trigger on a historically large deal.
IBM has been a poster child for a company moving through a painful transformation. As Box CEO (and IBM business partner) Aaron Levie put it on Twitter, sometimes a company has to make a bold move to push that kind of initiative forward:
They believe they can take their complex mix of infrastructure/software/platform services and emerging technologies like artificial intelligence, blockchain and analytics, and blend all of that with Red Hat’s profitable fusion of enterprise open source tools, cloud native, hybrid cloud and a keen understanding of the enterprise.
As Jon Shieber pointed out yesterday, it was a tacit acknowledgement that company was not going to get the results it was hoping for with emerging technologies like Watson artificial intelligence. It needed something that translated more directly into sales.
Red Hat can be that enterprise sales engine. It already is a company on a $3 billion revenue run rate, and it has a goal of hitting $5 billion. While that’s somewhat small potatoes for a company like IBM that generates $19 billion a quarter, it represents a crucial addition.
That’s because in spite of its iffy earnings reports over the last five years, Synergy Research reported that IBM had 7 percent of the cloud infrastructure market in its most recent report, which it defines as Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service and hosted private cloud. It is the latter that IBM is particularly good at.
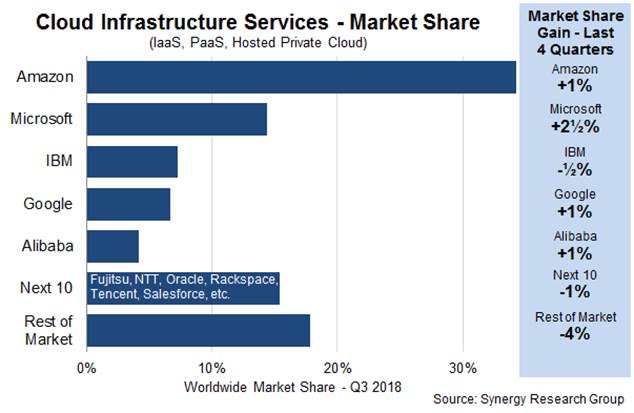
The company has the pieces in place now and a decent amount of marketshare, but Red Hat gives it a much more solid hybrid cloud story to tell. They can potentially bridge that hosted private cloud business with their own public cloud (and presumably even those of their competitors) and use Red Hat as a cloud native and open source springboard, giving their sales teams a solid story to tell.
IBM already has a lot of enterprise credibility on its own, of course. It sells on top of many of the same open source tools as Red Hat, but it hasn’t been getting the sales and revenue momentum that Red Hat has enjoyed. If you combine the enormous IBM sales engine and their services business with that of Red Hat, you have the potential to crank this into a huge business.

Photo: Ron Mller
It’s worth noting that the deal needs to pass shareholder muster and clear global regulatory hurdles before they can combine the two organizations. IBM has predicted that it will take at least until the second half of next year to close this deal and it could take even longer.
IBM has to use that time wisely and well to make sure when they pull the trigger, these two companies blend as smoothly as possible across technology and culture. It’s never easy to make these mega deals work with so much money and pressure involved, but it is imperative that Big Blue not screw this up. This could very well represent its last best chance to right the ship once and for all.
Forget Watson, the Red Hat acquisition may be the thing that saves IBM
With its latest $34 billion acquisition of Red Hat, IBM may have found something more elementary than “Watson” to save its flagging business.
Though the acquisition of Red Hat is by no means a guaranteed victory for the Armonk, N.Y.-based computing company that has had more downs than ups over the five years, it seems to be a better bet for “Big Blue” than an artificial intelligence program that was always more hype than reality.
Indeed, commentators are already noting that this may be a case where IBM finally hangs up the Watson hat and returns to the enterprise software and services business that has always been its core competency (albeit one that has been weighted far more heavily on consulting services — to the detriment of the company’s business).
Watson, the business division focused on artificial intelligence whose public claims were always more marketing than actually market-driven, has not performed as well as IBM had hoped and investors were losing their patience.
Critics — including analysts at the investment bank Jefferies (as early as one year ago) — were skeptical of Watson’s ability to deliver IBM from its business woes.
As we wrote at the time:
Jefferies pulls from an audit of a partnership between IBM Watson and MD Anderson as a case study for IBM’s broader problems scaling Watson. MD Anderson cut its ties with IBM after wasting $60 million on a Watson project that was ultimately deemed, “not ready for human investigational or clinical use.”
The MD Anderson nightmare doesn’t stand on its own. I regularly hear from startup founders in the AI space that their own financial services and biotech clients have had similar experiences working with IBM.
The narrative isn’t the product of any single malfunction, but rather the result of overhyped marketing, deficiencies in operating with deep learning and GPUs and intensive data preparation demands.
That’s not the only trouble IBM has had with Watson’s healthcare results. Earlier this year, the online medical journal Stat reported that Watson was giving clinicians recommendations for cancer treatments that were “unsafe and incorrect” — based on the training data it had received from the company’s own engineers and doctors at Sloan-Kettering who were working with the technology.
All of these woes were reflected in the company’s latest earnings call where it reported falling revenues primarily from the Cognitive Solutions business, which includes Watson’s artificial intelligence and supercomputing services. Though IBM chief financial officer pointed to “mid-to-high” single digit growth from Watson’s health business in the quarter, transaction processing software business fell by 8% and the company’s suite of hosted software services is basically an afterthought for business gravitating to Microsoft, Alphabet, and Amazon for cloud services.
To be sure, Watson is only one of the segments that IBM had been hoping to tap for its future growth; and while it was a huge investment area for the company, the company always had its eyes partly fixed on the cloud computing environment as it looked for areas of growth.
It’s this area of cloud computing where IBM hopes that Red Hat can help it gain ground.
“The acquisition of Red Hat is a game-changer. It changes everything about the cloud market,” said Ginni Rometty, IBM Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer, in a statement announcing the acquisition. “IBM will become the world’s number-one hybrid cloud provider, offering companies the only open cloud solution that will unlock the full value of the cloud for their businesses.”
The acquisition also puts an incredible amount of marketing power behind Red Hat’s various open source services business — giving all of those IBM project managers and consultants new projects to pitch and maybe juicing open source software adoption a bit more aggressively in the enterprise.
As Red Hat chief executive Jim Whitehurst told TheStreet in September, “The big secular driver of Linux is that big data workloads run on Linux. AI workloads run on Linux. DevOps and those platforms, almost exclusively Linux,” he said. “So much of the net new workloads that are being built have an affinity for Linux.”
The largest software acquisition ever: IBM to buy Red Hat for $34B
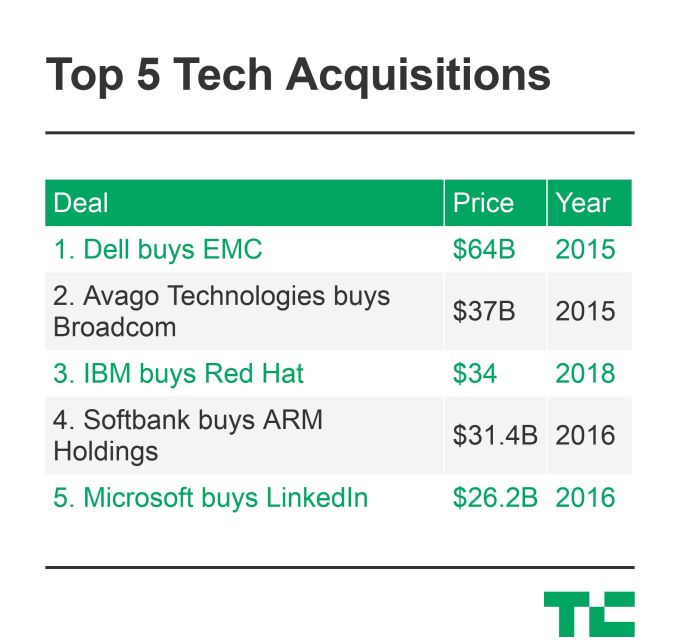
At a price typically reserved for semiconductor companies, telecoms, and pharmaceutical giants, IBM announced today it would pay a record $34 billion in cash and debt to acquire enterprise open source provider Red Hat. Eclipsing Microsoft’s $26.2 billion acquisition of LinkedIn, this is the biggest software acquisition in history. It’s not the biggest tech acquisition ever, though, as that title belongs to Dell’s $67 billion buyout of data storage business EMC.
You can learn about what IBM is buying Red Hat to become a hybrid cloud company in TechCrunch editor Ingrid Lunden’s deep dive here:
So how does the IBM-Red Hat deal (if it closes), stack up against the other largest acquisitions of all time?
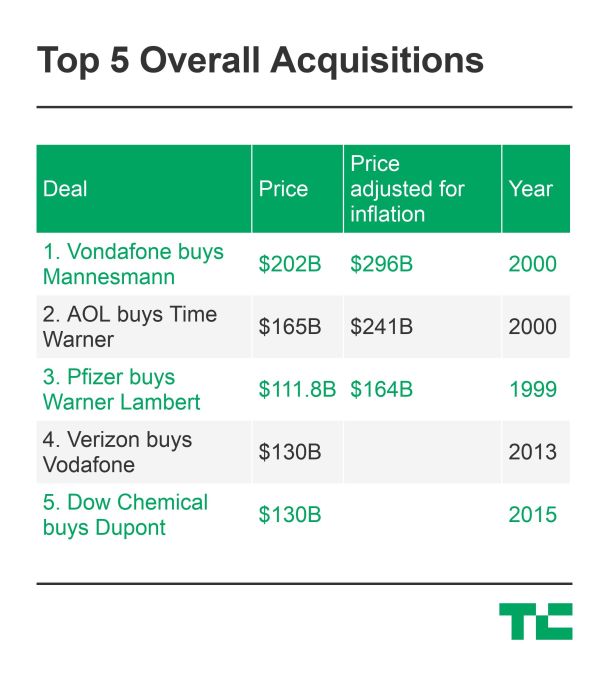
The Red Hat deal is proof that the scalability of software can massively concentrate wealth. Unlike industrial giants of old that split their fortunes with the physical resource providers that supplied and distributed their oil, chemical, or packaged good empires, software requires almost no material cost to create or distribute. The aggregation of value to software giants and their leaders offers both a great incentive to build a world-changing business, but also a drastic shift of capital out of the hands of labor. While it’s fine to celebrate Red Hat’s accomplishment, society must inevitably grapple with the poverty and populism fueled by how software funnels money to the few.
IBM to buy Red Hat for $34B in cash and debt, taking a bigger leap into hybrid cloud
After rumors flew around this weekend, IBM today confirmed that it would acquire open source, cloud software business Red Hat for $190 per share in cash, working out to a total value of $34 billion. IBM said the deal has already been approved by the boards of directors of both IBM and Red Hat but is still subject to Red Hat shareholder and regulatory approvals. If all goes as planned, the acquisition is expected to close in the latter half of 2019.
The deal is all about IBM, which has long continued to rely on its legacy server business, taking a bigger bet on the cloud, and very specifically cloud services that blend on-premises and cloud-based architectures — something that the two companies have already been working on together since May of this year (which now might be looked at as a test drive). Red Hat will be a distinct unit within IBM’s Hybrid Cloud team — which is already a $19 billion business for IBM, the company said — and it will continue to focus on open-source software.
“The acquisition of Red Hat is a game-changer. It changes everything about the cloud market,” said Ginni Rometty, IBM Chairman, President and Chief Executive Officer, in a statement. “IBM will become the world’s number-one hybrid cloud provider, offering companies the only open cloud solution that will unlock the full value of the cloud for their businesses.”
The combined businesses will be able to offer software in services spanning Linux, containers, Kubernetes, multi-cloud management, and cloud management and automation, IBM said. IBM also added that together the companies will continue to build partnerships with multiple cloud providers, including AWS, Microsoft’s Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba and others, alongside the IBM Cloud.
As Josh Constine notes here, it’s one of the biggest-ever tech acquisitions, and arguably the biggest that is dedicated primarily to software. (Dell acquired EMC for $67 billion, to pick up software but also a substantial hardware and storage business.)
While companies like Amazon have gone all-in on cloud, in many cases, a lot of enterprises are making the move gradually — IBM cites stats that estimate that some 80 percent of business workloads “have yet to move to the cloud, held back by the proprietary nature of today’s cloud market.” Buying Red Hat will help IBM better tap into an opportunity to address that.
“Most companies today are only 20 percent along their cloud journey, renting compute power to cut costs,” she continued. “The next 80 percent is about unlocking real business value and driving growth. This is the next chapter of the cloud. It requires shifting business applications to hybrid cloud, extracting more data and optimizing every part of the business, from supply chains to sales.”
On top of that, it will give IBM a much stronger footing in open source software, the core of what Red Hat builds and deploys today.
“Open source is the default choice for modern IT solutions, and I’m incredibly proud of the role Red Hat has played in making that a reality in the enterprise,” said Jim Whitehurst, President and CEO, Red Hat, in a statement. “Joining forces with IBM will provide us with a greater level of scale, resources and capabilities to accelerate the impact of open source as the basis for digital transformation and bring Red Hat to an even wider audience – all while preserving our unique culture and unwavering commitment to open source innovation.”
While IBM competes against the likes of Amazon, the companies will see to remain partners with them with this acquisition. “IBM is committed to being an authentic multi-cloud provider, and we will prioritize the use of Red Hat technology across multiple clouds” said Arvind Krishna, Senior Vice President, IBM Hybrid Cloud, in a statement. “In doing so, IBM will support open source technology wherever it runs, allowing it to scale significantly within commercial settings around the world.”
IBM said that Red Hat will add to its revenue growth, gross margin and free cash flow within 12 months of closing.