Usage-based pricing (UBP) is on the rise — 61% of SaaS companies used this model in some form in 2022, VC firm OpenView found out.
UBP consists of charging based on how the service or product is consumed, not on how many people are using it; that would be the seat-based approach.
But as often in pricing, things are more blurred, and many companies are actually using blended models. Think of Zapier, for example: It offers subscription tiers that include consumption as one of its main variables.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money.
Read it every morning on TechCrunch+ or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
That blending is one of the key findings of OpenView’s State of Usage-Based Pricing report: “It’s not usage-based or subscription pricing. Today SaaS companies are turning to more complex, hybrid models,” the authors wrote.
Now in its second edition, the firm’s report is based on responses collected between July and August 2022 from private SaaS companies. That was a few months ago, so the data may be lagging a bit, but it still reflects the new spirit in which founders find themselves.
 We know it does because that’s the same survey sample as the Chargebee-OpenView SaaS benchmarks report we covered last November, and the findings already showed a drastic mood change compared to 2021. For instance, an overwhelming majority of respondents said they would be slashing spending regardless of cash runway.
We know it does because that’s the same survey sample as the Chargebee-OpenView SaaS benchmarks report we covered last November, and the findings already showed a drastic mood change compared to 2021. For instance, an overwhelming majority of respondents said they would be slashing spending regardless of cash runway.
When it comes to UBP, there’s more continuity because adoption keeps on rising. However, the effects of a recession — and of what the report refers to as the “SaaS crash” — are visible, too, although with some surprises.
Today, we are sharing some thoughts based on our chat with two of the report’s co-authors, OpenView partner Sanjiv Kalevar and operating partner Kyle Poyar.
These considerations also tie into a recent conversation we had on sales tools for product-led growth (PLG) with Justin Dignelli, CEO and co-founder at Pace. Indeed, according to OpenView, “monetizing based on usage is part of a broader shift towards PLG.” Let’s dive in.
Progressive adoption and hybrid models
A 61% adoption of UBP represents a significant increase. In 2021, 45% of the respondents said they were using this pricing model, up from 34% in 2020.
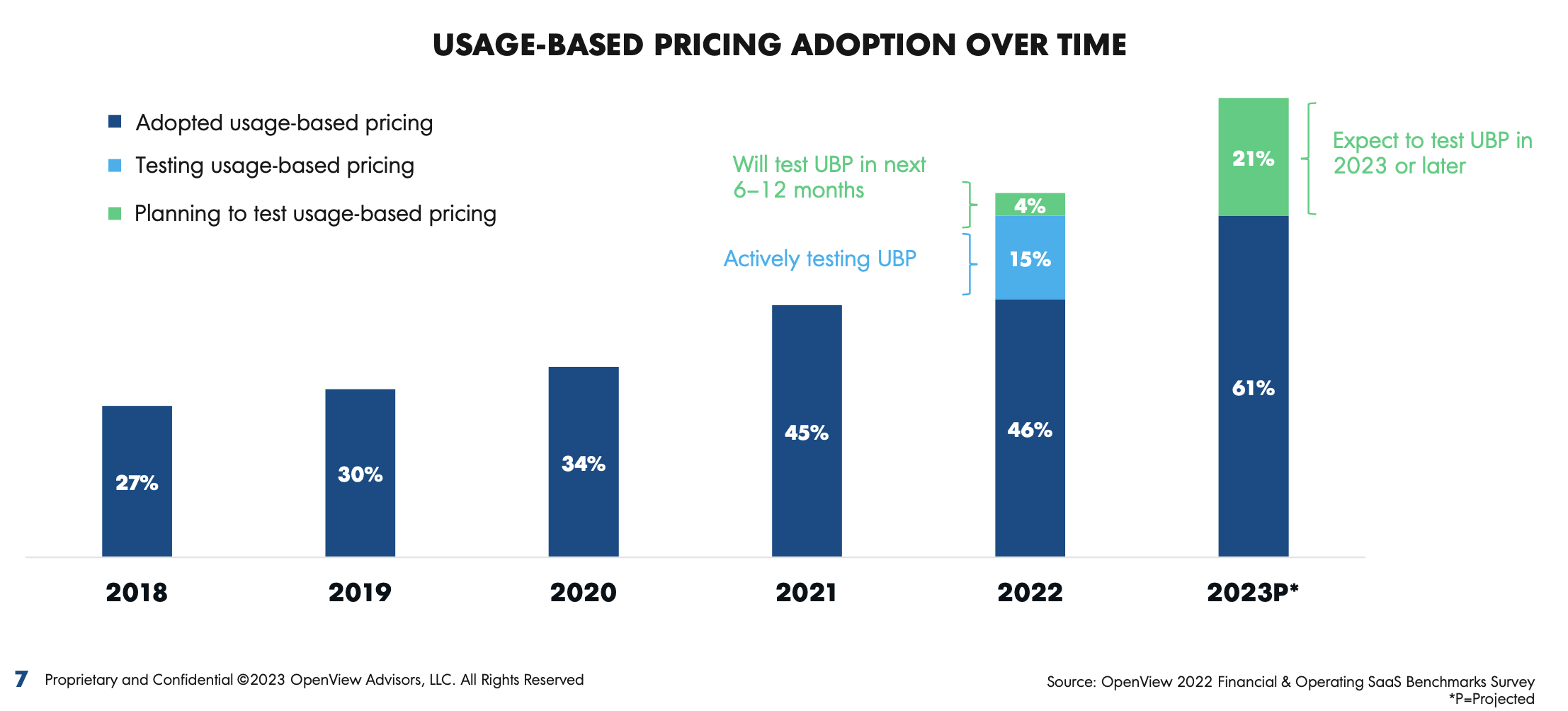
Image Credits: OpenView
That usage-based pricing grew in adoption is notable in itself: Companies often feel anxious about changing their pricing in a recession and may feel that UBP is less predictable than more traditional models, such as multiyear commitments.
However, these fears can often be overcome by understanding that UBP doesn’t have to replace the previous model(s). After all, companies can try it out first — 15% of the respondents said they were actively testing it, and another 4% said they would do so in the next six to 12 months.
Even after this testing period, UBP can still be part of a hybrid model. “As software companies get more ambitious around the problems they solve for their customers, we have to expect some level of complexity in pricing,” Poyar said.
This complexity in pricing is also creating opportunities for B2B startups focusing on problems such as metering and billing in a product-led environment. OpenView refers to these as “the modern pricing tech stack,” a topic we’ll explore further shortly.
Image Credits: OpenView
Today, we’ll focus on a more pressing issue: Are UBP adopters faring better than their peers? As we explored recently, PLG companies seem to currently be less profitable than their sales-led peers, so we are curious to know how UBP acts as a variable.
Still ahead
My favorite chart of the report relies on PitchBook data to compare the median revenue growth rate of public SaaS companies depending on their pricing models: usage-based or subscription-based.
As you can see in the graph below, around 2019, UBP companies tended to grow faster than their peers and outperformed them even more in 2021, when the software sector was shining.
However, the gap narrowed significantly in recent months; in Q1 of this year, UBP companies were only 4% ahead in terms of revenue growth (and that’s not even touching on profitability).
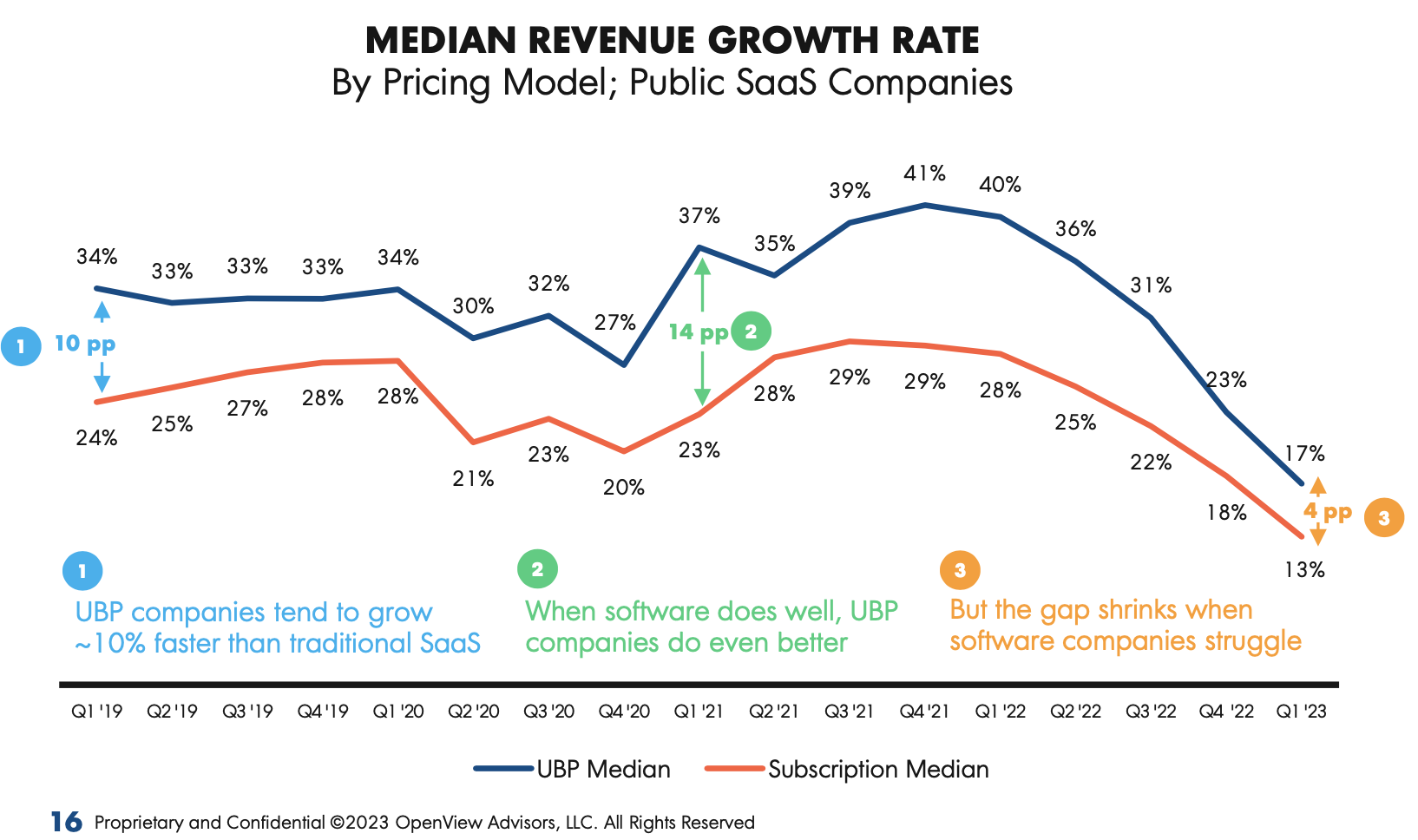
Image Credits: OpenView
OpenView’s Kalevar doesn’t think the contraction is surprising. However, he said, “What some people might find surprising is that usage-based companies were still growing faster, on average, than their traditional subscription peers. […] The fact that they’re still growing faster, even in a recession, despite no contracts and very little commitment, speaks to that model.”
Usage-based pricing is clearly more directly aligned with the customer’s current needs, but that’s also what makes it more volatile. Hence these three recommendations from OpenView:
- Know it’s coming: Usage-based pricing growth rates will overreact when businesses are spending and when businesses cut.
- Invest in predictability: Develop the right in-house financial and analytic group to identify early signs of contraction/expansion.
- Keep CAC flexible: Keep an eye on how much of your CAC can be flexed up (in good times) and down (in bad times).
Reading this reminded me of my recent chat with Justin Dignelli, CEO of Pace, a startup that helps companies adapt to the rise of product-led sales. Here’s what he had to say on UBP:
Usage-based pricing has become really popular in recent years. I think a big part of that has to do with AWS, [which] I would argue is the biggest PLG company in the world. They really conditioned folks to want that type of experience.
Usage-based pricing makes it much more important to understand the state of the customer in detail. You have to ask questions like: Will they be a customer tomorrow? Can you get them to use more of what they’re using today tomorrow? Can you get net new projects? […]
I think more and more customers will demand usage-based pricing, which means the onus to understand retention and expansion for sellers and [customer success] folks will be that much more important on a day-to-day basis.
It is true that infrastructure was ahead of other sectors in terms of adopting usage-based models. But, OpenView noted, “they’re now found in horizontal and vertical application software as well.”
Poyar and Kalevar both said that vertical software will be worth watching in terms of UBP adoption. “It is lower than in other categories right now, but I see more and more companies adopting that [model],” Kalevar told TechCrunch, adding that “there’s a growing class of vertical API companies” that are a good fit for this model. This also sounds like an interesting trend for us to track.
