In the first installment of our Cloud Quarterly report series, we spoke about how the market has shifted to valuing cloud companies’ profitability, even when it comes at the expense of growth (this thread on Twitter goes in-depth into that data).
There is no shortage of efficiency metrics that cloud executives can track to gain a better perspective of their overall economics. Sales and marketing efficiency metrics such as LTV-to-CAC, CAC payback and the magic number have long been mainstays in board decks and fundraising materials. As the market has turned, burn multiple (net burn / net new ARR) has emerged as a popular, all-encompassing way of looking at burn versus ARR growth.
The difficulty with these efficiency metrics, though, is that they aren’t tangible in a way that is actionable for your employees. They feel more like financial metrics than operational ones, and it is difficult for employees to execute against these concepts.
Improvements in product can absolutely have a large impact on sales efficiency, but those improvements are a derivative of product and engineering work rather than something that can feel top-of-mind. Burn multiple puts the emphasis on having “less bad burn” rather than indicating which actions will actually drive profitability.
It is still imperative to be the winner in your market.
Our advice for cloud CEOs? At your next all-hands meeting, or during your next one-on-ones with functional leaders, align your team around ARR per employee — a metric we are calling APE.
APE is an extremely simple metric we think could serve as your North Star as you navigate these volatile times.
Why should APE be the efficiency North Star?
The cost structure of cloud companies is driven primarily by people. There are other costs to be mindful of, such as cloud expenses, real estate and spending on other SaaS applications you need to run your business. But around 70% of your costs are likely going to relate directly to your employees. If you want your business to become more efficient, at the end of the day, your employee base is the place to start.
One key point here: Optimizing your employee base should ideally come through smart, measured hiring, not a reactive reduction in force. Achieving the former will help your business avoid the latter. When attempting to instill this hiring discipline across your organization, APE can be a powerful tool.
As a manager or executive, every decision you make has an impact on APE. Every new initiative or project that needs to be staffed impacts APE. Every backfilled role impacts APE. If you can automate a task with software, or spread new projects between team members, your APE improves. Before any personnel-related move is made, APE should be discussed.
Some key benchmarks to keep in mind
Unlike the magic number or the “Rule of 40,” there is no one APE number we recommend. The APE of a company with all employees co-located in the Bay Area, for example, needs to be much higher to reach profitability than a company that has employees in lower-cost geographies.
But we can offer some data points to help guide you, all derived from Capital IQ data and Battery research through many years scaling software businesses.

Image Credits: Battery Ventures
At giant and profitable tech companies like Google and Meta, the APE number is significantly higher than their public cloud comps: $1.7 million at Google and $1.4 million at Meta (using MRQ revenue x 4 in the numerator as a proxy for ARR).
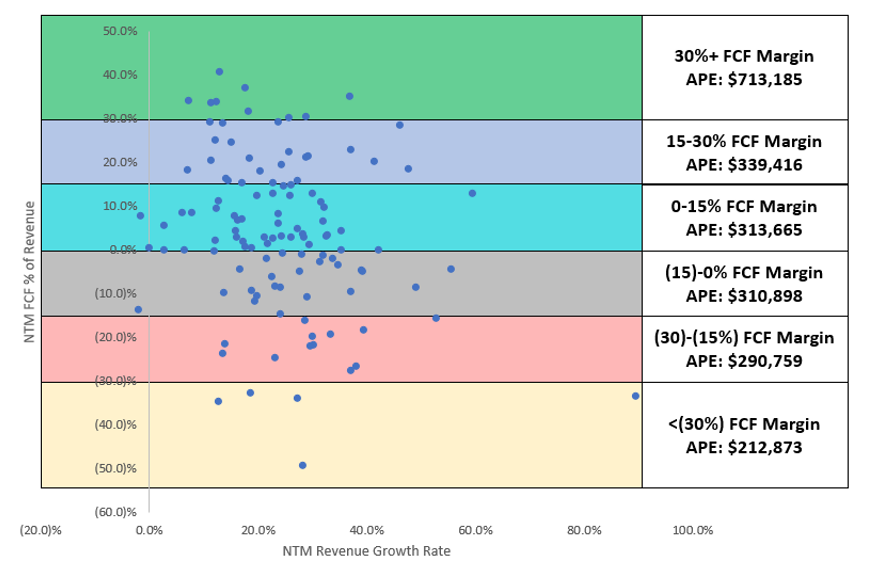
Image Credits: Battery Ventues
Meanwhile, the APE figures for smaller, privately held SaaS businesses are typically much lower. You might be a bit surprised at how far off you are from these comps. A Series B company with $5 million in ARR and 80 employees would have an APE of just $63,000; a Series D-stage company with $50 million in ARR and 300 employees would have an APE of just under $167,000.
If you’re still far away from these public benchmarks, that’s OK and normal. Based on our pattern recognition, below are the APE ranges we generally recommend targeting by ARR scale (with caveats around gross margin, geographic location, balance sheet and forecasted growth rate):
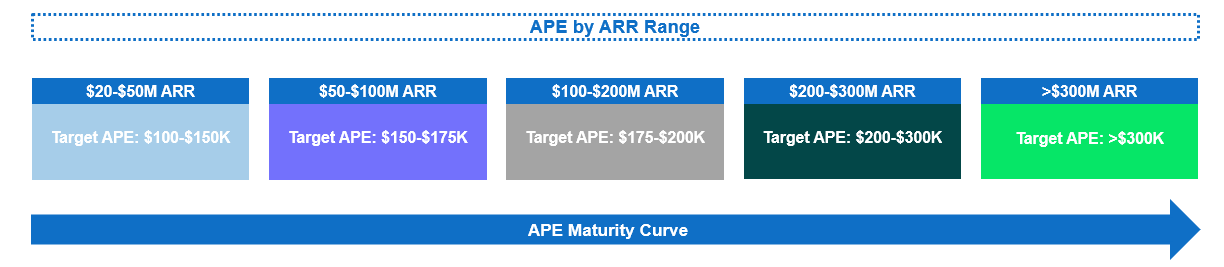
Image Credits: Battery Ventures
Getting to a higher APE earlier in the maturity cycle is likely a net positive. Overall, we believe a goal of getting to $200,000 would serve most midstage/late-stage growth companies well.
However, that’s still not enough to break even, which we discuss next.
Tracking your Breakeven APE (and why this should be in every deck)
The calculation for Breakeven APE is: total expenses/employee.
Total expenses should include not just personnel costs, but all expenses. We think that employee count is best looked at as a point-in-time measure rather than an average over some period.
CEOs should be aware of their Breakeven APE and closely track this number. This metric can be very different across companies — we’ve seen as low as $150,000 and as high as $450,000. Bill.com, for example has an APE over $450,000 but isn’t breakeven yet on a P&L basis; Ceridian HCM has an APE of just $160,000 but is free-cash-flow positive.
We would advise not to include stock-based compensation (SBC) in this calculation, since that is a non-cash expense that does not impact cash flow breakeven. That is not to say that SBC does not matter; on the contrary, it is highly impactful in building shareholder value and is often under-appreciated. A Breakeven APE that includes SBC would be much higher, but we would encourage companies to track the intermediate milestone of Breakeven APE excluding SBC first.
It is worth noting that Breakeven APE is on the rise. Most companies are not fully aware of how fast Breakeven APE is rising in the current inflationary environment.
The fully loaded cost of an employee has gone up substantially over the last 10 years at cloud companies. In our estimate, Breakeven APE has gone from around $180,000 a decade ago to about $250,000 today, with some companies now at or above $300,000.
Founders should not make the modeling assumption that “total expenses per employee” is constant, and that raising APE alone is enough to get to profitability. You must actively discuss strategies to keep Breakeven APE in check over time (e.g., hiring in low-cost locations or shifting employee mix to have the appropriate level of entry employees/salaries).
At the end of the day, market leadership still matters
While it is important for companies to take a deeper look at their efficiency in the current market, it is critical to be thoughtful about how they achieve that efficiency.
It is still imperative to be the winner in your market. The nature of your market matters: If you are in a highly competitive, horizontal product-market space (say, developer tooling) versus a niche, vertical SaaS market where you have limited competition, you’ll need to think differently about your APE with respect to where you are in your company’s journey.
Employee experience is also still important. You want to build a company where great talent wants to work and feels supported. Culture absolutely still matters.
If you raised money once (or twice!) in 2021 and have years of cash in the bank, austerity likely is not prudent but greater discipline likely is. You can drive Breakeven APE lower by automating repetitive tasks or simplifying your employee perks program (many “perk point solutions” have less than 10% utilization).
In conclusion
Our advice is to start focusing on current and Breakeven APE today, particularly if your ARR is north of $20 million.
Take a look at your current APE and where your financial model puts you at the end of the year. If your model has your APE declining year over year, you should take a long, hard look at your model. Ideally, the company should be able to make significant progress on APE each year.
Ultimately, your company will not be valued as a multiple of your APE but the discounted value of your future cash flows. But you need to have a North Star metric that will help your team lead you there. We believe APE is the most elegant metric around which to reorient, and it can be the center of your all-hands presentations over time.
Current APE and Breakeven APE provide the near-term goal posts, and the targets in the table above can help as reference points for the next chapter of the journey.
Disclaimer: Battery Ventures provides investment advisory services solely to privately offered funds. Battery Ventures neither solicits nor makes its services available to the public or other advisory clients. For more information about Battery Ventures’ potential financing capabilities for prospective portfolio companies, please refer to our website.
For a full list of all Battery investments, please click here. No assumptions should be made that any investments identified above were or will be profitable. It should not be assumed that recommendations in the future will be profitable or equal the performance of the companies identified above.
Content obtained from third-party sources, although believed to be reliable, has not been independently verified as to its accuracy or completeness and cannot be guaranteed. Battery Ventures has no obligation to update, modify or amend the content of this post nor notify its readers in the event that any information, opinion, projection, forecast or estimate included, changes or subsequently becomes inaccurate.
