It was only a matter of time.
As more tech companies go public, the necessary disclosure has meant that with access to more information on the financial condition of many startups, mainstream investors have begun questioning just how profitable and sustainable these startups are.
Naturally, this has resulted in some skepticism, and tech firms around the world are slowly changing how they function to address these concerns.
At Jungle Ventures, we have observed the following key trends in how the startup ecosystem is evolving:
Moving beyond demand-side innovation
Building a defensible moat is essential for the long-term success of any startup. For undifferentiated tech-enabled services like food delivery or mobility, user exclusivity is challenging to attain, as the user base is rather flirtatious and has low to no switching costs. In such cases, innovating just to meet customer demand might not be enough. It is interesting to note that startups are now focusing on supply-side innovation to build a long-term competitive advantage.
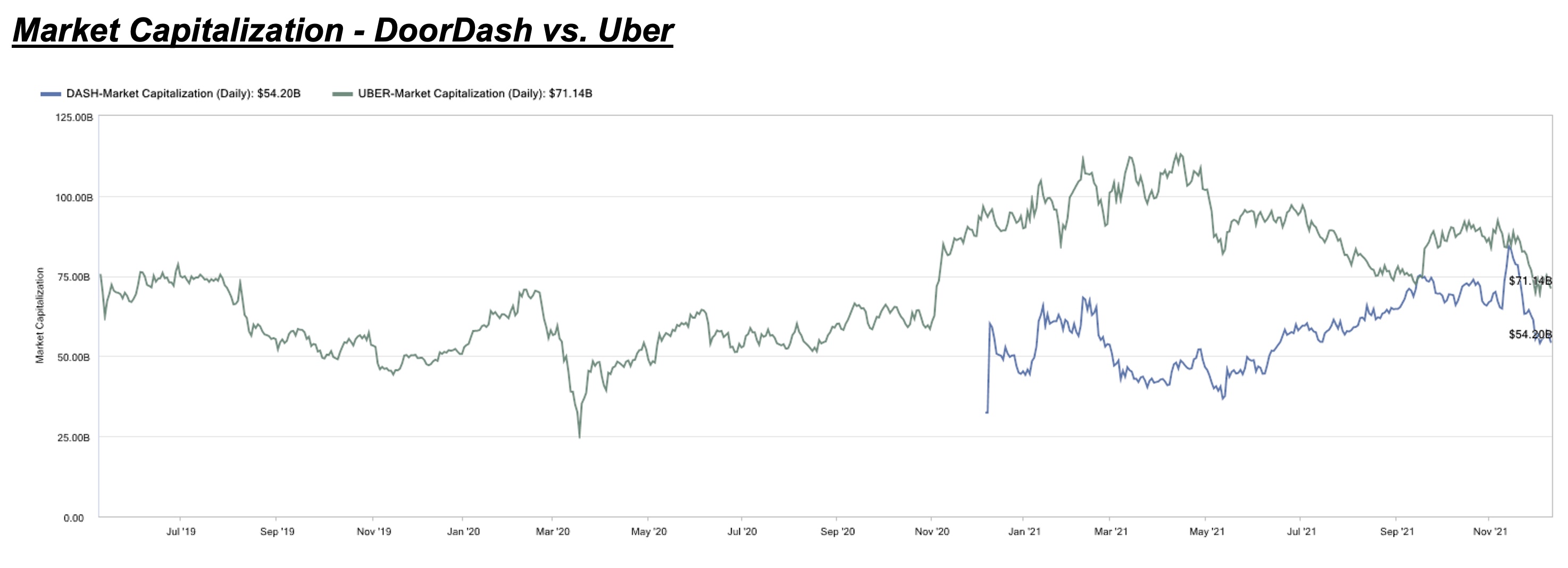
One of these success cases is DoorDash, which has managed to edge out Grubhub and catch up with Uber Eats despite being relatively late to the food delivery scene in the U.S. Instead of just focusing on user (demand-side) acquisition, DoorDash has launched several services to empower its restaurant partners and help them grow their businesses.
For example, DoorDash Drive is a white-label, flat-fee delivery service that lets merchants generate their own orders and use DoorDash to execute deliveries.
The pandemic has also made founders and investors realize the importance of building a resilient business.
We also have DoorDash Storefront, which allows restaurants to create their own online stores (on DoorDash) for pick-up and delivery orders. It provides restaurants with customer data, which other third-party delivery platforms usually do not share.
Such initiatives and value-added offerings helped DoorDash increase its restaurant partnerships (supply-side) and exclusivity, which, in turn, improves user retention and engagement.
Indian food delivery company Zomato also has a similar merchant/B2B initiative called Hyperpure, a one-stop procurement solution that supplies fresh, hygienic, quality ingredients directly to restaurant partners from farmers, producers, mills, etc.
Although Hyperpure represents a small part of revenue (about 10% of its total revenue in fiscal year 2020), the company is planning to invest more than $50 million in the business in the next 18 to 24 months.
Zomato is planning to offer more services to its restaurant partners, similar to DoorDash, to foster stronger partnerships. The company is currently in talks with restaurant point-of-sale players and e-vehicle fleet operators. One of its long-term strategies is to invest in companies in the food ecosystem.
Creating an ecosystem of offerings to maximize value
Startups have long been advised to focus on one problem and be the best at solving it. Lately, though, we are seeing tech companies developing an ecosystem of offerings to help address different, but related, pain points for their customers.
One of the major benefits of having an ecosystem for users is convenience, as they do not have to switch between different platforms and apps for solutions. For companies, this could open new revenue sources, help them gain more user insight, and cultivate greater loyalty and retention.
On the surface, Airbnb might seem like a platform to match property hosts and guests. But behind it, there is a whole ecosystem of services and offerings that support owners in hosting their properties on the platform.
For example, it has an insurance program (Host Protection Insurance) for hosts, and its trust and safety initiatives help hosts perform background checks and risk scoring on guests, prevent fraud and scam, etc. Various complementary startups and third-party businesses are also there to complete Airbnb’s ecosystem and address property owners’ pain points.
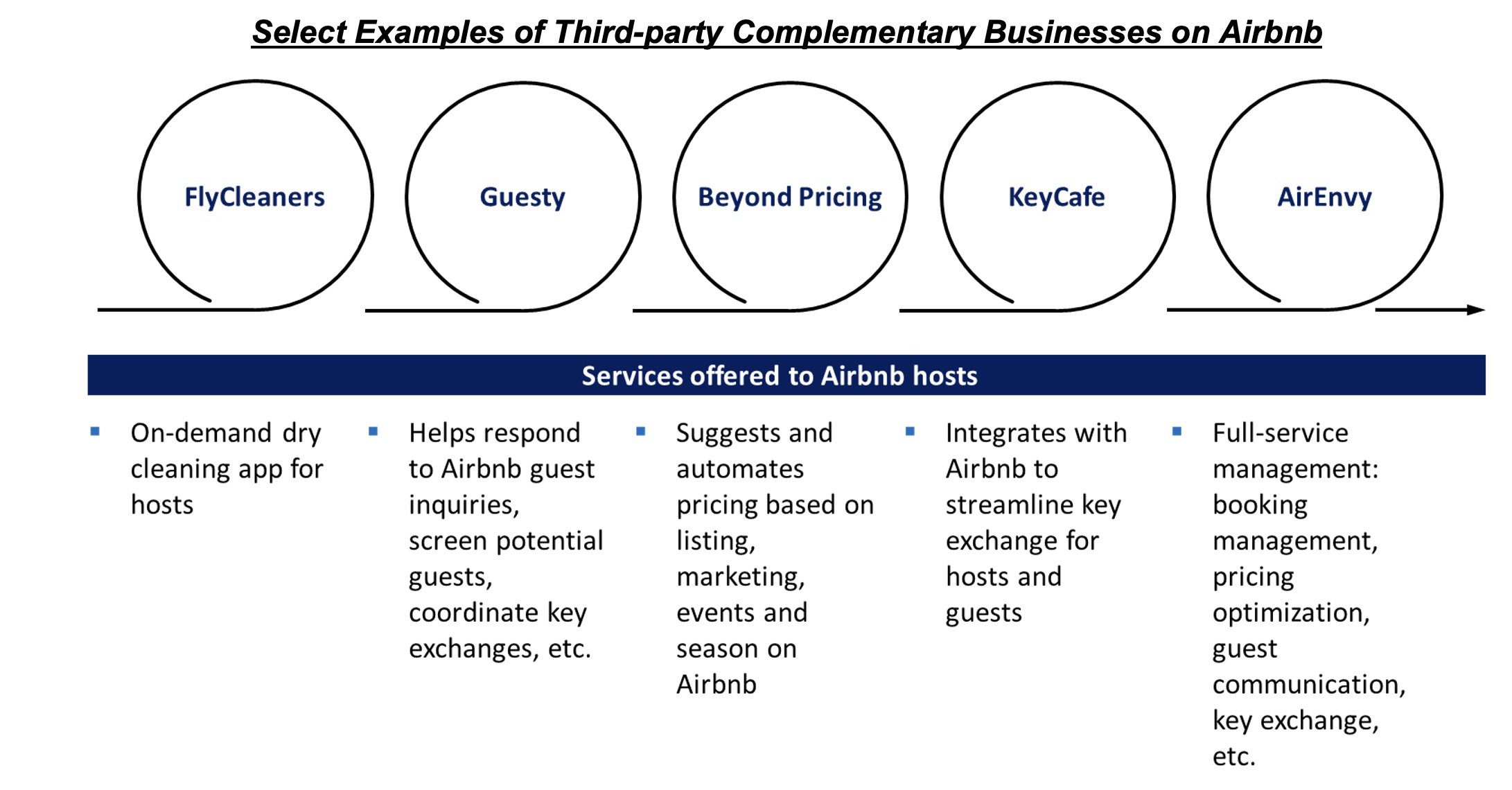
Image Credits: Jungle Ventures
In India, Razorpay has been building an ecosystem of services that cater to SMEs instead of just being a payment gateway and infrastructure for merchants — its initial core product. The following is a snapshot of its ecosystem and current services, which aim to assist merchants in managing and growing their businesses.
The company’s ecosystem benefits from these services, as they attract businesses and clients who have different needs. This allows Razorpay to maximize the value of its offerings over time.
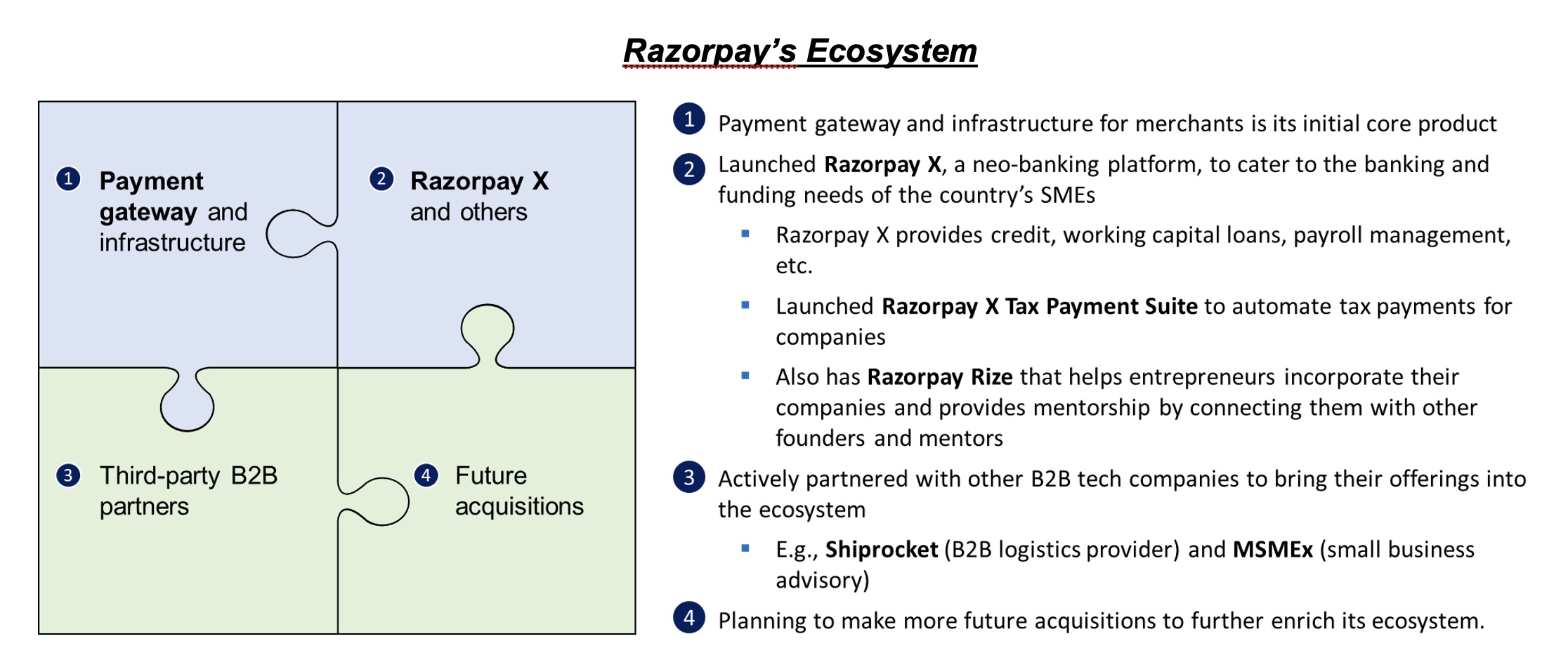
Image Credits: Jungle Ventures
Similarly, in Southeast Asia, Nium has become the first B2B payment unicorn in the region thanks to its “payment + ecosystem” business model. The company initially focused solely on international payments, and while cross-border payment infrastructure is still its core product, Nium has expanded to offer a full suite of banking-as-a-service solutions for its corporate customers. Customers now use Nium’s platform for international payments, card issuance, payment collections and so on.
Accelerating profitable non-core operations
The pandemic has also made founders and investors realize the importance of building a resilient business.
Moving on from pursuing growth at all costs, companies are building more synergistic offerings from non-core operations that have higher margins compared to their core businesses. This helps them improve their profitability as a whole so the business can be more sustainable in the long run without having to rely only on external capital.
The trend is most apparent among more established tech companies since they have a user base that can be further monetized via additional offerings.
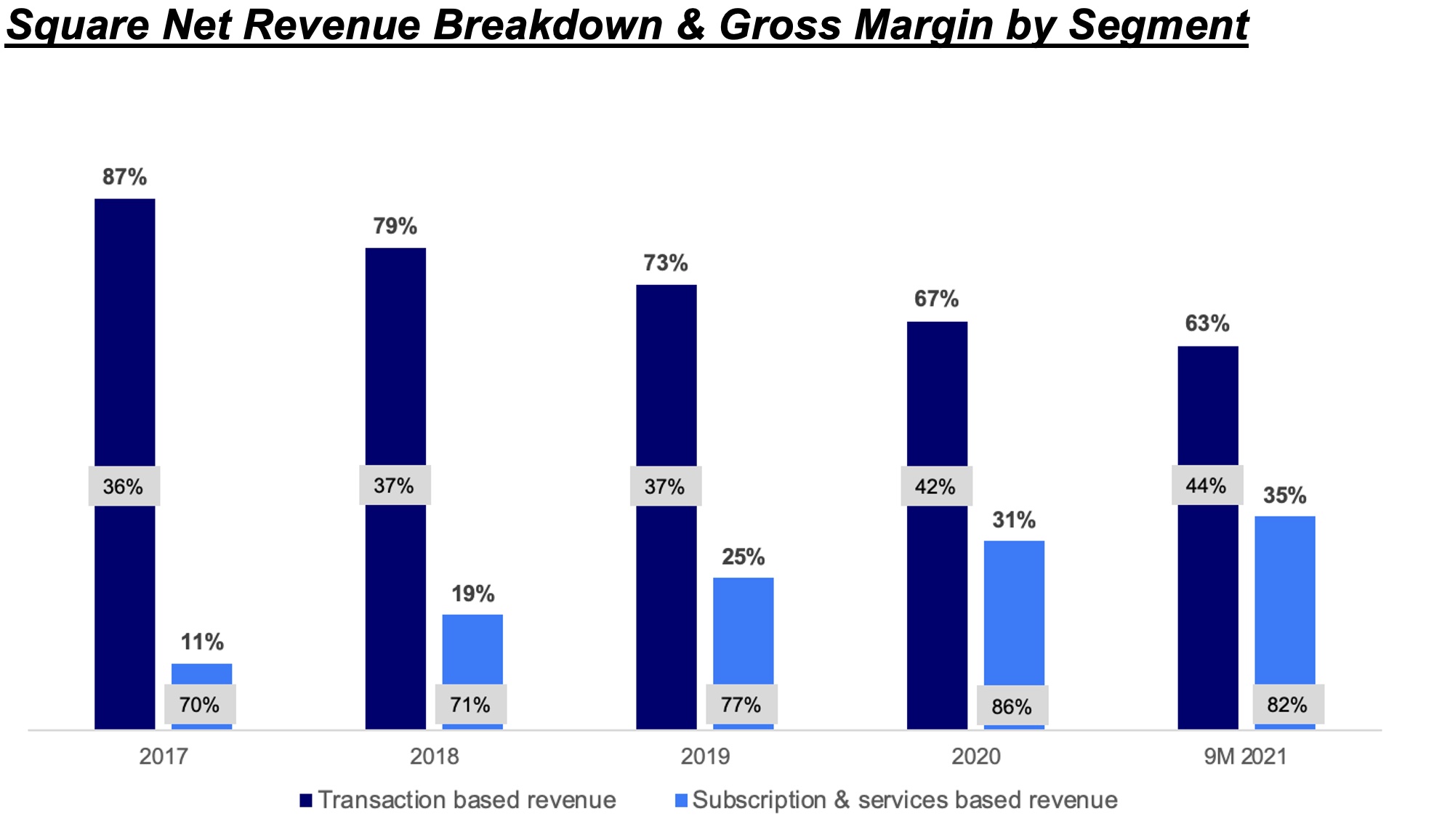
For example, Block (formerly known as Square), which generates most of its revenue by processing payments and transactions, has expanded its offerings to provide subscriptions and services. These include software subscriptions by sellers, an Instant Deposit function that allows both customers and sellers to instantly deposit funds into their bank accounts, and Square Card (a prepaid Visa card).
Block’s subscription and services segment operates at almost double the gross margins (82%) compared to its transaction-based services (44%), and we are seeing a steady increase in its contribution to business — up from 11% in 2017 to 35% in the first nine months of 2021.
Sourced from company financial reports. Note: Net revenue excludes Bitcoin revenue. Figures in gray boxes indicate gross margins. Image Credits: Jungle Ventures
In Southeast Asia and India, a few leading tech firms have embraced this approach lately, but as many of their initiatives launched not too long ago, the impact on their overall business models is yet to be seen.
For example, Grab’s enterprise and new initiatives segment was launched in 2018 with GrabAds, an advertising and marketing service for merchants. In 2020, the company launched GrabDefence, which provides fraud detection and prevention tech to third-party businesses.
What does it mean for startups?
In our opinion, these three trends — whether it is about boosting profitability from non-core operations, focusing on supply-side innovation, or maximizing value by building ecosystems — point to one common theme: being more sustainable and resilient.
Instead of chasing growth, founders and management should consider building a more sustainable business rather than just focusing on raising the next round of capital.
