Usage-based pricing (UBP) has quickly gone from fringe to mainstream in SaaS. Converts to UBP are drawn to the promise of accelerated revenue growth and a more efficient land-and-expand business model.
But achieving faster revenue growth isn’t as simple as just changing pricing. UBP is a company-wide effort and requires ditching the old SaaS metrics playbook.
One way to think about usage-based revenue is that it’s product-led growth (PLG) in its purest form.
Consider Snowflake, a data warehousing company that went public in 2020 and now has a $100 billion market cap. While conventional wisdom suggests SaaS companies should aspire for net retention of 100% or greater, Snowflake reports an off-the-charts 169% net retention driven by an effective consumption-based pricing model. The company’s net retention actually rose from 158% in Q2 of fiscal 2021.
For Snowflake, $1,000 in initial spend from a new customer would theoretically turn into $13,000+ after five years. So how much should I spend on customer acquisition (CAC) to acquire a new logo? Do I compensate sales for the initial spend, or should reps share in that customer growth? How should I invest in product and engineering to ensure customers see better value as their costs increase?
Many usage-based companies ask themselves similar questions.
Usage-based companies share their customers’ success
Leading usage-based companies have the phenomenal ability to grow with their existing customers at extremely high rates. Top-quartile net retention for those with a largely usage-based pricing model was 122% compared to those with usage-based subscription tiers (110%) or no usage-based pricing (109%), according to OpenView data.
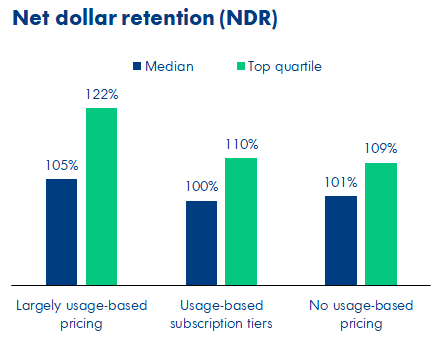
Image Credits: OpenView Partners
But such an expansion isn’t usually a result of selling more products or gating advanced features behind up-sell packages. It comes from customers increasing their consumption as they become more successful and discover new use cases.
For example, Twilio boasts a 132% net retention rate across an impressive base of 200,000+ active customers, and about 85% of Twilio’s net expansion comes from usage with only 15% coming from new products, according to the company’s 2020 investor presentation.
The best-performing usage-based companies instill a customer success mindset across every team. Product and engineering teams carve out dedicated product and UX resources to focus on product adoption. Marketing provides the tools and community that inspires users to adopt more of the product. And pricing tends to be as simple as possible — New Relic, for example, decided to give away valuable features that lead to greater stickiness, and therefore, higher lifetime value.
Product becomes a revenue-generating expense
Conventional wisdom dictates that SaaS companies grow primarily by spending money on sales and marketing. In the usage-based approach, growth is often skewed toward existing customers and investments in products that increase adoption can be directly connected to revenue growth.
It’s perhaps unsurprising that usage-based companies have a far higher ratio of R&D spend relative to sales and marketing than their traditional subscription peers. The median ratio in the data was 1.5x for companies with a largely UBP model compared to 1.0x for those with usage-based subscription tiers and 0.8x for those without UBP.
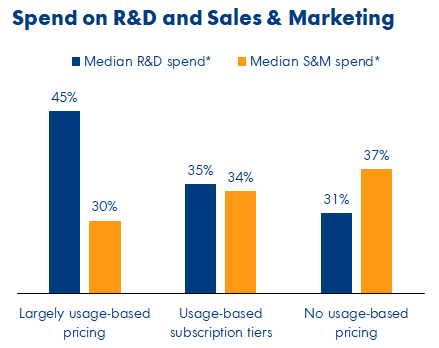
Image Credits: OpenView Partners
One way to think about usage-based revenue is that it’s product-led growth (PLG) in its purest form. In fact, 92% of usage-based companies said they expect to increase their PLG investments in 2022. Key PLG investment areas include “try before you buy” offerings, product analytics tooling and product growth experimentation.
Logz.io, a cloud observability company, doubled down on its self-service offering while leaning further into UBP. Allowing people to try the product on their own and then buy with a pay-as-you-go model reduced conversion friction and let users estimate their needs before creating a monthly or annual contract.
Self-service started out as an experiment with only two engineers but has since grown into a powerful growth lever. In just a year after launching self-service, Logz.io found that the channel accounted for 50% of their new customers, and that self-service customers grew their spend by an average of 300% over the course of their first year.
Be mindful of margins
Cost structure shouldn’t drive a company’s pricing — customer value should. That said, UBP can be explained to customers more easily if a company has a cost that goes with it (think: Stripe or AWS costs). Usage models also minimize the risk of ending up with lots of unprofitable customers in the event that a SaaS company does have high COGS.
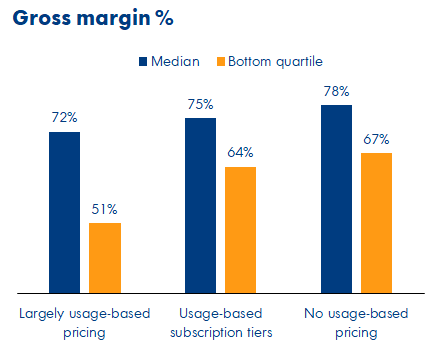
Image Credits: OpenView Partners
For those with high COGS, UBP may be imperative. In fact, companies with gross margins of less than 60% were especially likely to adopt a largely UBP model. The median usage-based company had a gross margin of 72%, lower than peer companies, and the bottom quartile had a gross margin of 51% or lower, according to the data.
Below average margins aren’t necessarily an impediment to growth. In many cases, SaaS companies will be able to improve their product gross margins as they reach greater scale and can negotiate their cloud agreements. That said, be mindful of avoiding unforced errors such as lack of discipline over discounting or introducing all-you-can-eat pricing for power users, both of which can quickly eat into profitability.
