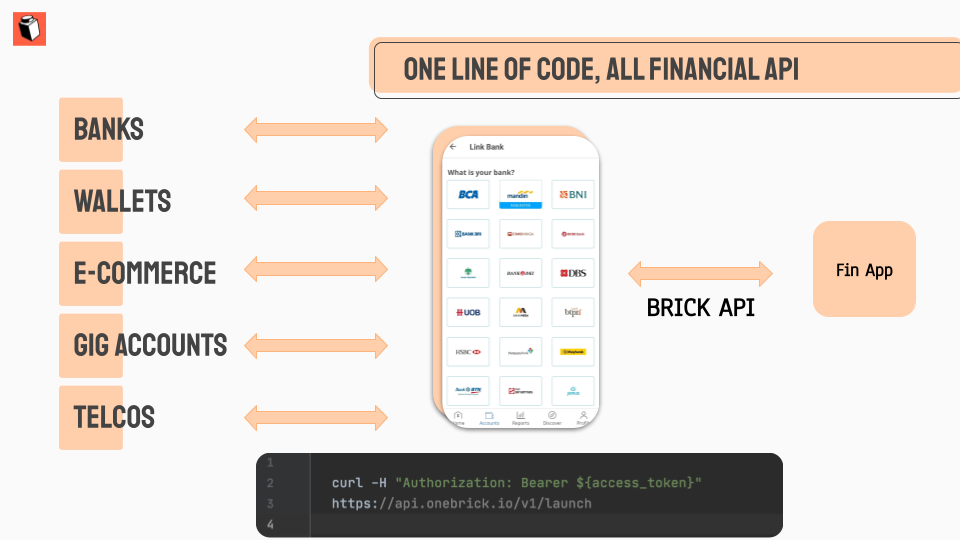
The adoption of financial apps is surging in Southeast Asian markets like Indonesia, the region’s most populous country. Founded by fintech veterans last year, Brick develops APIs that make it easier for tech companies to add identity verification and access financial data from their users. It is currently partnered with Indonesia’s seven largest banks, covering more than 90% of the country’s bank accounts, and plans to expand into all Southeast Asia countries.
More than three-fourths of Southeast Asia’s population is unbanked or underbanked, meaning they don’t have a bank account or access to traditional lending services. Brick will serve them as well, with products like mobile wallet and telcos APIs that are currently in beta and slated for launch next quarter.
The startup, which is now used by 250 developers and 35 tech companies, announced today it has raised a new seed round. The amount of funding was undisclosed. Investors include investment firms Better Tomorrow Ventures, PT Prasetia Dwidharma, 1982 Ventures, Antler and Rally Cap Ventures, and angel backers like TrueLayer chief operating officer Shefali Roy, Cred chief executive officer Kunal Shah, Modalku CEO Reynold Wijaya, Carousell CEO Quek Siu Rui, and the founders of Nium, Xfers, Aspire, BukuWarung, ZenRooms and CareemPay.
Brick was founded in 2020 by chief executive officer Gavin Tan, an early employee at Aspire, a neobank for small to mid-sized businesses, and chief technology Deepak Malhotra, previously co-founder of Indian neobank Slice and a former PayPal engineer.
Brick’s APIs have been deployed by personal financial management, cloud accounting, lending, wealth management and neobank apps, and Tan told TechCrunch it also sees use cases in verticals like savings, stock trading and financial planning.
Tan said he began thinking of launching Brick while working at high-growth fintech startups in Southeast Asia, including Aspire, and encountering a lack of infrastructure that slowed product development.
“Without unified APIs like those provided by Brick, fintech developers have to spend months figuring out commercials, navigating differing tech standards and navigating differing data standards, before they are able to launch their app,” Tan said.
Brick and other fintechs have benefited from strong support from Indonesian regulators. For example, Bank Indonesia published open banking API standards in 2020.
Tan said the standards “represents concrete government recognition of open banking principles, including consumer ownership of data and the necessity of their consent to transfer and use that data (which Tan describes as “a core principle that all our products adhere to”) and establishing a common language for banks and fintechs that enables the adoption of embedded finance. It also laid out implementation timelines for open APIs, beginning with payment initiation APIs in 2021, which Brick will launch later this year.
Brick works closely with Bank Indonesia and Indonesia’s Financial Services Authority and is participating in Bank Rakyat Indonesia’s Sembrani Wira accelerator program.
The most obvious comparison for Brick is to Plaid, the financial API provider that helped enable the adoption of open banking and open finance in the United States, Canada and European countries. A key difference, however, is that Plaid serves markets where the majority of people have a bank account.
On the other hand, “in Southeast Asia, only 25% of adults regularly use a bank account,” Tan said. “For the 75% unbanked and underbanked adults, their data resides in alternative financial data sources.” To tap into that market, Brick is building APIs for alternative financial data sources, like mobile wallets, telcos, utility providers, e-commerce platforms, social security and tax offices.
The company is currently focused on product launches in Indonesia, and plans to start expanding into other high-growth fintech markets, including Singapore, the Philippines and Vietnam, later this year.