One of the most active and notorious data-stealing ransomware groups, Maze, says it is “officially closed.”
The announcement came as a waffling statement, riddled with spelling mistakes and published on its website on the dark web, which for the past year has published vast troves of stolen internal documents and files from the companies it targeted, including Cognizant, cybersecurity insurance firm Chubb, pharmaceutical giant ExecuPharm, Tesla and SpaceX parts supplier Visser and defense contractor Kimchuk.
Where typical ransomware groups would infect a victim with file-encrypting malware and hold the files for a ransom, Maze gained notoriety for first exfiltrating a victim’s data and threatening to publish the stolen files unless the ransom was paid.
It quickly became the preferred tactic of ransomware groups, which set up websites — often on the dark web — to leak the files it stole if the victim refused to pay up.
Maze initially used exploit kits and spam campaigns to infect its victims, but later began using known security vulnerabilities to specifically target big-name companies. Maze was known to use vulnerable virtual private network (VPN) and remote desktop (RDP) servers to launch targeted attacks against its victim’s network.
Some of the demanded ransoms reached into the millions of dollars. Maze reportedly demanded $6 million from one Georgia-based wire and cable manufacturer, and $15 million from one unnamed organization after the group encrypted its network. But after COVID-19 was declared a pandemic in March, Maze — as well as other ransomware groups — promised to not target hospitals and medical facilities.
But security experts aren’t celebrating just yet. After all, ransomware gangs are still criminal enterprises, many of which are driven by profit.
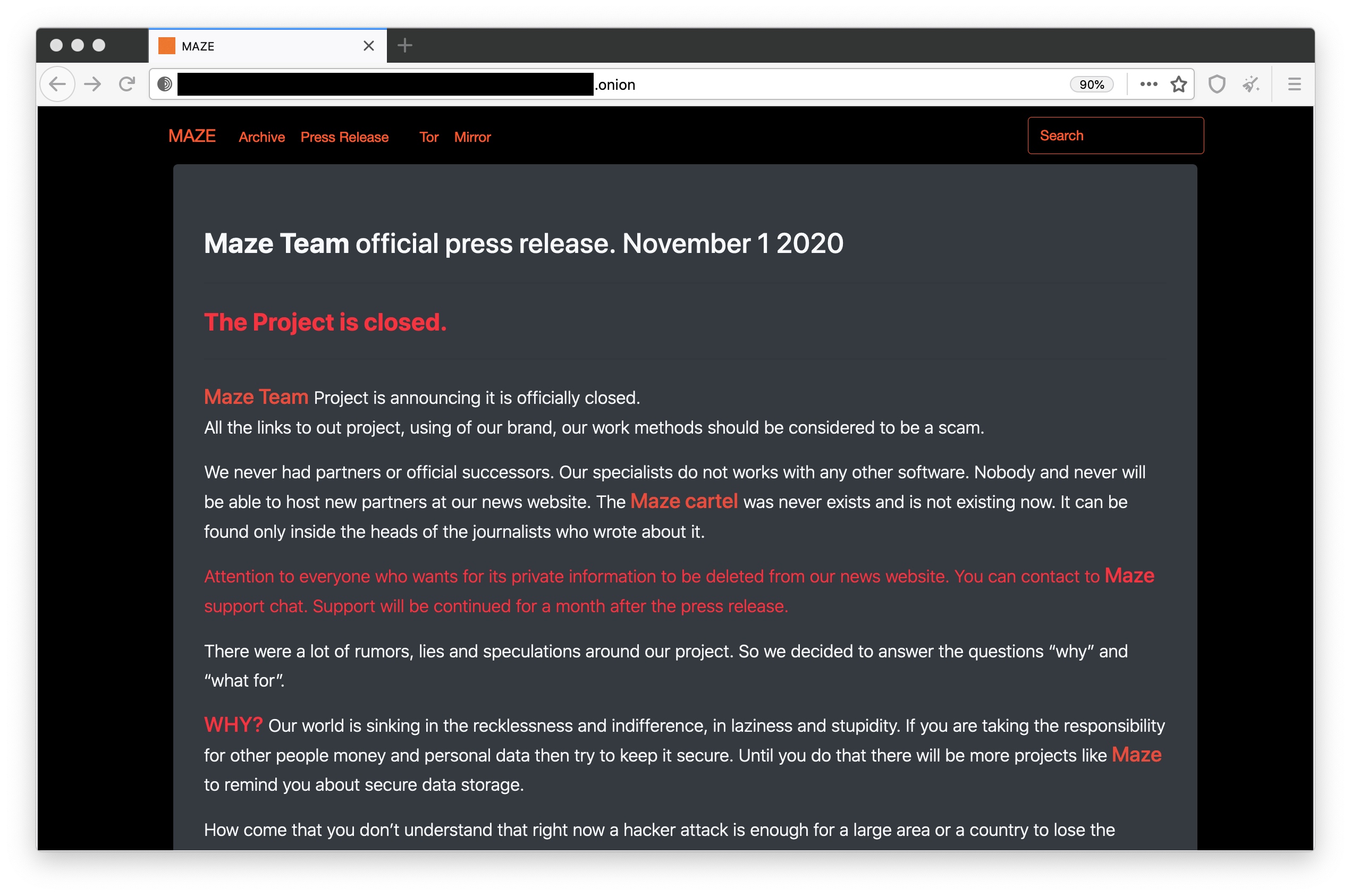
A statement by the Maze ransomware group, claiming it has shut down. Screenshot: TechCrunch
“Obviously, Maze’s claims should be taken with a very, very small pinch of salt,” said Brett Callow, a ransomware expert and threat analyst at security firm Emsisoft. “It’s certainly possible that the group feels they have made enough money to be able to close shop and sail off into the sunset. However, it’s also possible — and probably more likely — that they’ve decided to rebrand.”
Callow said the group’s apparent disbanding leaves open questions about the Maze group’s connections and involvement with other groups. “As Maze was an affiliate operation, their partners in crime are unlikely to retire and will instead simply align themselves with another group,” he said.
Maze denied that it was a “cartel” of ransomware groups in its statement, but experts disagree. Steve Ragan, a security researcher at Akamai, said Maze was known to post on its website data from other ransomware, like Ragnar Locker and the LockBit ransomware-for-hire.
“For them to pretend now that there was no team-up or cartel is just plain backwards. Clearly these groups were working together on many levels,” said Ragan.
“The downside to this, and the other significant element, is that nothing will change, Ransomware is still going to be out there,” said Ragan. “Criminals are still targeting open access, exposed RDP [remote desktop protocol] and VPN portals, and still sending malicious emails with malicious attachments in the hope of infecting unsuspecting victims on the internet,” he said.
Jeremy Kennelly at FireEye’s Mandiant threat intelligence unit said that while the Maze brand may be dead, its operators are likely not gone for good.
“We assess with high confidence that many of the individuals and groups that collaborated to enable the Maze ransomware service will likely continue to engage in similar operations — either working to support existing ransomware services or supporting novel operations in the future,” said Kennelly.
