SOS Venture’s biotech accelerator IndiBio held its first ever demo day today. The event held in downtown San Francisco showcased startups working on some pretty wild science projects like 3D printed animal parts, artificial skin and bioreactors to make better beer. So without further ado, here’s the rundown of the first 11 startups to debut from IndieBio:
Clara Foods – aims to make a better egg white than chickens can make – in a lab. This process means manipulating the DNA of yeast to make a purer, but a genetically identical egg white to what chickens produce. The company maps genes for functionality and performance so that the proteins look, act and taste just like chicken egg whites, but foam better and can be used to improve foods. “Imagine the world’s fluffiest meringue,” founder … said onstage.
He pointed out the time, cost and intensive work as well as environmental damage it takes to get egg whites the natural way.
Clara Foods egg whites use 5x’s less water, have more protein and can be denser, according to the startup. Clara Foods is working with some of the world’s largest egg white users, such as Barilla. It plans to make revenue through these partnerships and by selling the individual proteins used to create the product.

The team from Arcturus BioCloud
Arcturus BioCloud – gives science hobbyists the ability to gene splice their way to super bacteria with a few clicks on their laptop. It hand-built it’s own bio server machine to carry out multiple experiments and get results very fast. It is now building its second machine.
The startup also hosts a library of DNA fragments created by users. The business model is to market each test for $80. More than 300 users in 165 countries have run tests on the platform since launching in May. Arcturus is now seeking Series A financing.
Pembient – Makes rhinoceros horns without the rhinoceros using DNA and a 3D printer. As we wrote in an earlier TechCrunch post about the launch of this startup, that’s good news for the rhinos of the world. There are only five northern white rhinos left, and the Western black rhinoceros, which was thought to be extinct in 2006, is now officially extinct.
The startup is reproducing rhino horns as well as skincare products associated with the rhino horn. It plans to expand to printing body parts of other endangered species in the future, including elephant tusks and tiger bones.
It also announced onstage that it launched the Black Rhinoceros Genome Project on crowdfunding site Experiment.com to raise money that will allow them to sequence the genes and bring back the Western black rhino population.
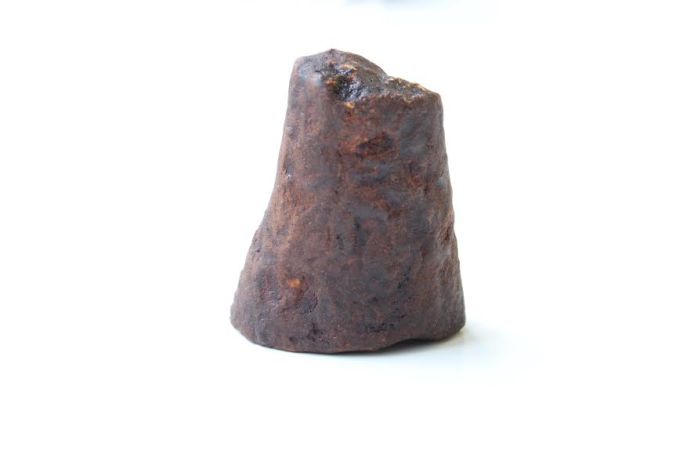

3D printed genetically identical rhino horn grown in Pembient’s lab space at IndieBio.
Ranomics – More than half of your genetic test results contains information that scientists can’t understand. This startup aims to interpret all genetic variations for any human disease gene. It does this by creating the world’s first comprehensive functional variant database solely dedicated to resolving variants of unknown significance (VUS) in genetic tests.
Ranomics has been working with Color Genomics, 23andMe and others to work on this problem. The startup is now going to the prenatal testing space and said it expects to be the number one testing space for all variant genomics by 2020.
Zymochem – creates biotechnology solutions to help chemical companies produce materials from renewable sources. Chemical production is a $2.4 trillion industry. Zymochem hopes to be competitive with major chemical corporations like Dow Chemical to create nylon from sugars rather than oil.

Sensa.io founders.
Sensa.io – Makes bioreactors. “Beer is as old as humanity, itself,” co-founder Francesco Capodieci said onstage. He compares the natural fermentation process to what the startup aims to do for much more expensive and complicated bioreactors. The startup has created a low-cost, open solution to let the community decide what the bioreactor will do, whether it be making kombucha or cheese from yeast.
Bioloom – Creates material from engineered bacteria that promises to heal wounds faster than cotton bandages. The material is a microbial cellulose to start growing artificial skin and creates a scaffold for drug delivery. It has cut fermentation time in the process by 50 percent, according to the company. The hydrogel dressing produced by Bioloom easily adheres and feels like your own skin. It is a medical product that does not need FDA approval. The plan is to get the low-cost product out to the market by next year.
abiobot – Helps lower the cost and time of scientific breakthroughs by building robots that automate the process. The robots use built-in cameras to make the robots smarter, more flexible and reactive to assist scientists. The startup is in the prototype stage for its robot lab assistant. The startup is working in collaboration with Arcturus BioCloud to create a larger lab that goes beyond the desktop. It also has plans to work with a lab in Beijing, China.
Blue Turtle Bio – Creates engineered gut microbes that are capable of secreting the required enzymes needed for helping those suffering from certain diseases. The startup puts the bacteria into a pill to allow patients to swallow and get the bacteria into a habitat where it can grow. This process replaces the enzyme, but not the defective gene. It has the potential to improve the health and quality of life for patients with certain diseases. It also dramatically lowers the cost of enzyme replacement therapy.
The company has yet to test on human subjects, but is currently running tests to demonstrate that the microbial protein can pass through the gut into the bloodstream.
Blue Turtle plans to work with giant drug companies such as Pfizer in the future.
extem – creates stem cells. We are facing a stem cell crisis, and there aren’t enough donor stem cells to go around for research, according to the startup. This is a $29 billion market and is expected to grow exponentially. The extem platform allows it to create billions of stem cells using more than 10,000 donors. The startup said it is building the largest donor bank for stem cells in the world.
Orphidia – Aims to transform healthcare with in-home medical lab testing using the Orphidia System. This system holds 5 patents and works with portable diagnostics tools to assess the health of your blood and other bodily fluids that are then digitally sent to the physician. The startup hopes to compete with lab testing by making testing convenient and in the home. It’s a b2b business model and each chip on the system costs $5 that the startup resells for $20. The FDA regulatory process is a Class2 510(k), meaning it will be able to launch by 2017.
Affinity (not included at the original time of publishing) – Creates a manufacturing platform that is working on drastically cutting the cost of producing biopharmaceutical drugs, specifically, in antibody therapeutics such as the Rituxan cancer drug, that harness one’s own immune system to fight diseases.
One third of the pharmaceutical sector’s revenue is expected to arise from these immunotherapy drugs in the next ten years, and 8 of the 10 bestselling drugs today are immunotherapeutics. Unfortunately, these drugs currently cost hundreds of thousands of dollars to produce, so the patients that need these drugs can’t get them.
Affinity plans to take 25% market share in the next five years.

