 Editor’s note: Adam Nash is the chief operating officer of Wealthfront, a SEC-registered, software-based financial advisor located in Palo Alto. He was formerly executive-in-residence with Greylock Partners and VP of product management at LinkedIn. Follow him on his blog and on Twitter at @AdamNash.
Editor’s note: Adam Nash is the chief operating officer of Wealthfront, a SEC-registered, software-based financial advisor located in Palo Alto. He was formerly executive-in-residence with Greylock Partners and VP of product management at LinkedIn. Follow him on his blog and on Twitter at @AdamNash.
“Bubbles are beautiful, fun and fascinating, but do you know what they are and how they work? Here’s a look at the science behind bubbles.” — About.com Chemistry, “Bubble Science”
“Double, double toil and trouble
Fire burn, and cauldron bubble.” — Macbeth, Act 4, Scene 1
Given the incredible volatility we’ve seen lately in the Bitcoin and gold markets, there has been a resurgence in discussion about bubbles. This topic is always top of mind in Silicon Valley, especially given that the two favorite local topics of conversation are technology companies and housing.
Defining a market bubble is actually a bit trickier than it might first appear. After all, what differentiates the inevitable booms and busts involved in almost any business and industry from a “bubble”?
The most common definition of a speculative or market bubble is when a broad-based, surging euphoria or wave of optimism carries asset prices well beyond supportable value. The canonical bubble was the tulip mania of the 1630s, but it extends across history and countries all the way up to the Internet bubble of the late 1990s and the housing bubbles in the past decade.
What Do Bubbles Look Like?
Not surprisingly, there are a number of great frameworks for thinking about this problem.
In 2011, Steve Blank and Ben Horowitz debated in The Economist whether or not technology was in a new bubble. In those posts, Steve cited the research of Jean-Paul Rodrigue denoting four phases of a bubble: stealth, awareness, mania and blow-off.
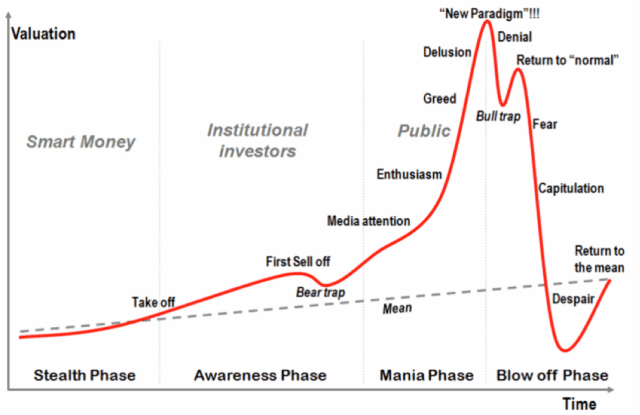
(Source: Wikipedia)
How Do Bubbles Happen?
In 2000, Edward Chancellor published an excellent history and analysis of market bubbles over four centuries and a wide variety of countries called “Devil Take the Hindmost: A History of Financial Speculation.” In his book, he finds at least two consistent ingredients.
Uncertainty. In almost every bubble, there seems to be some form of innovation or insight that forces people to rapidly debate the creation of new economic value. (Yes, even tulip bulbs were once an innovation, and the product was incredibly unpredictable.) This uncertainty is typically compounded by some form of lottery effect, exacerbating early pay-offs for the first actors. Think back to stories about buying a condo in Las Vegas and flipping it in months for amazing gains. This creates the inevitable upside/downside imbalance that Henry Blodget recently framed as: “If you lose your bet, you lose 100%. If you win your bet, you make 1000%.” Inevitably, this innovation always leads to a shockingly large assessment of how much value could be created by this market.
Leverage/Liquidity. In every bubble, there is some form of financial innovation that broadly increases both leverage and liquidity. This is critical, because the expansion of leverage not only provides massive liquidity to fund the expansion of the bubble, but the leverage also sets up the covenants that inevitably unwind when the bubble turns aggressively to the downside. In some ways, it’s also inevitable. When a large number of people believe they’ve found a sure thing, logic dictates they should borrow cheap money to maximize their returns. In fact, the belief it may be a bubble can make them even greedier to lever up their investment so they can “cash out” the most before the inevitable break.
Behavioral Finance Lessons in Bubbles
Bubbles clearly have an emotional component, and to paraphrase Dan Ariely, humans may be irrational, but they are predictably irrational.
There are five obvious attributes of components of bubble psychology that play into market manias:
- Anchoring. We hear a number, and when asked a value-based question, even unrelated to the number, they gravitate to the value that was suggested. We hear gold at $1,500, and immediately in the aggregate we start thinking that $1,000 is cheap and $2,000 might be expensive.
- Hindsight Bias. We overestimate our ability to predict the future based on the recent past. We tend to over-emphasize recent performance in our thinking. We see a short-term trend in Bitcoin, and we extend that forward in the future with higher confidence than the data would mathematically support.
- Confirmation Bias. We selectively seek information that supports existing theories, and we ignore/dispute information that disproves those theories. (This also tends to explain most political issue blogs and comment threads.)
- Herd Behavior. We are biologically wired to mimic the actions of the larger group. While this behavior allows us to quickly absorb and react based on the intelligence of others around us, it also can lead to self-reinforcing cycles of aggregate behavior.
- Overconfidence. We tend to over-estimate our intelligence and capabilities relative to others. Seventy-four percent of professional fund managers in the 2006 study “Behaving Badly” believed they had delivered above-average job performance.
The greater fool theory posits that rational people will buy into valuations that they don’t necessarily believe, as long as they believe there is someone else more foolish who will buy it for an even higher value. The human tendencies described above lead to a fairly predictable outcome: After an innovation is introduced and a market is formed, people believe both that they are among the few who have spotted the trend early, and that they will be smart enough to pull out at the right time.
Ironically, the combination of these traits predictably leads to these four words: “It’s different this time.”
It’s Different This Time
After two massive bubbles in the U.S. in less than a decade, many people question spotting bubbles ahead of time is so difficult. In every bubble, a number of people do correctly identify the bubble. As in the story of the boy who cried wolf, however, the truth is apt to be disbelieved. The problem is that in every market, there are always people claiming that prices are too high. That’s what makes a market. As a result, the cry of “bubble” is far more often proven wrong than right.
Every potential bubble, however, provides an incredibly valuable frame for deepening and debating the role of human psychology in financial markets. Honestly and thoughtfully examining your own behavior through a bubble, and comparing it to the insights provided by behavioral finance, can be one of the most valuable tools an investor has to learning about themselves.