As electronics become more advanced, we approach a point where normal materials like copper simply cannot take the heat. For computing to get any faster, better cooling solutions will be needed — we’ve known this for a while. GE recently announced that their scientists at the GE Global Research Center have discovered a new thermal material that is a major breakthrough.
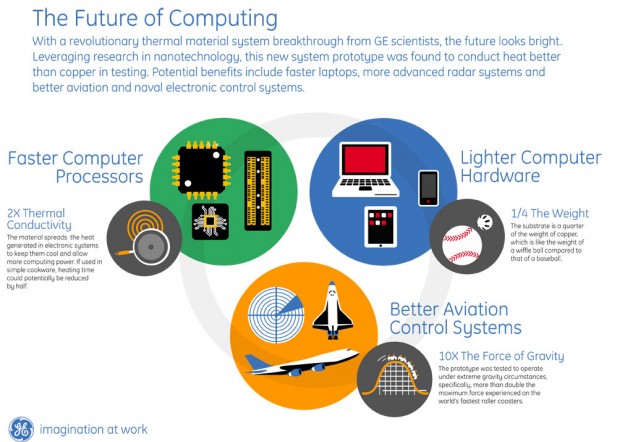
The new material could pave the way to faster computers, more advanced radar systems, and better aviation equipment — though you can bet it will make its way into defense equipment before computers.
GE developed a prototype substrate from its Nanotechnology Advanced Technology Program that can improve electronic cooling significantly. Also, when compared to copper, GE’s substrate is a quarter the weight, spreads heat twice as fast, and can operate at 10x the force of gravity. It’s been known that material science would be a huge factor in furthering Moore’s law, and if the science turns out, it looks as though GE has quite a head start.
Press Release
NISKAYUNA, N.Y., March 15, 2011 – Scientists in GE’s Global Research Center have demonstrated an advanced thermal material system that could pave the way to faster computing and higher performing electronic systems. Leveraging technologies developed under GE’s Nanotechnology Advanced Technology Program, they have fabricated a prototype substrate that can cool electronic devices such as a laptop computer twice as well as copper.
Since the dawn of the electronics age, copper has been a preferred material to cool electronics because of its favorable heat conducting properties. But as electronic systems become more advanced, they are generating more and more heat. Too much heat can limit the overall performance of these systems, impacting computing speed and processing power. New breakthrough materials will be needed to enable more advanced systems and applications.
The development of GE’s prototype substrate, which utilizes phase-change-based heat transfer, is part of a four year, $6 million program funded by the Defense Advanced Research Program Agency (DARPA, Contract # No. N66001-08-C-2008). As the leading organization of the program, GE Global Research has been collaborating with GE Intelligent Platforms, the Air Force Research Laboratory, and University of Cincinnati on the project.
Dr. Tao Deng, a senior scientist at GE Global Research and the project leader, said, “As electronics become more advanced, we are approaching the point where conventional materials like copper can’t take the heat. For computing to go faster and electronics systems to become more capable, better cooling solutions such as GE’s prototype substrate will be required to allow this to happen.”
Deng added, “In demonstrations, GE’s prototype substrate has functioned effectively in a variety of electronics application environments. We also subjected it to harsh conditions during testing and found it could successfully operate in extremely high gravity applications.”
Deng noted that GE’s prototype operated in conditions experiencing more than 10 times the normal force of gravity. By comparison, this gravity force is more than twice the maximum force experienced on the world’s fastest roller coasters.
How it Works
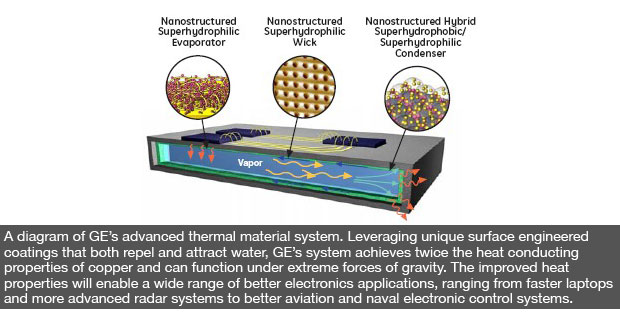
GE’s phase-change based prototype substrate can be applied to computer chips and a variety of different electronic components. It acts as a cooling mechanism that spreads or dissipates the heat generated in electronic systems to keep components cool.
During testing at the Air Force Research laboratories, GE’s research team successfully demonstrated a prototype substrate that was measured to have at least twice the thermal conductivity as copper at only one–fourth of its weight. In addition, the prototype successfully operated in a condition that was more than 10 times normal gravity.
With high thermal conductivity, low weight, and high “G” acceleration performance, this substrate could work well in a variety of different systems, ranging from laptop computers to larger scale, more sophisticated computing systems that run the avionics and electronic control systems on board jetliners and other aircraft.
In collaboration with various agencies from the US government, GE Global Research has been developing several advanced thermal technologies. Besides the DARPA effort, Dr. Deng is also leading a team, supported by Air Force Research Laboratory, to develop advanced thermal solutions for high-speed flight in a 1.5-year, $1 MM effort. These efforts will build a total thermal solution platform to serve multiple GE businesses, including GE Aviation, GE Energy, and GE Intelligent Platforms.
About GE Global Research
GE Global Research is the hub of technology development for all of GE’s businesses. Our scientists and engineers redefine what’s possible, drive growth for our businesses, and find answers to some of the world’s toughest problems.